1. AI-Powered Diagnostics
- Tools like ChatGPT and specialized algorithms assist doctors in analyzing symptoms, predicting diseases, and recommending treatments. AI is especially useful in radiology, pathology, and cardiology.
- Example: IBM Watson Health, DeepMind’s AI systems.
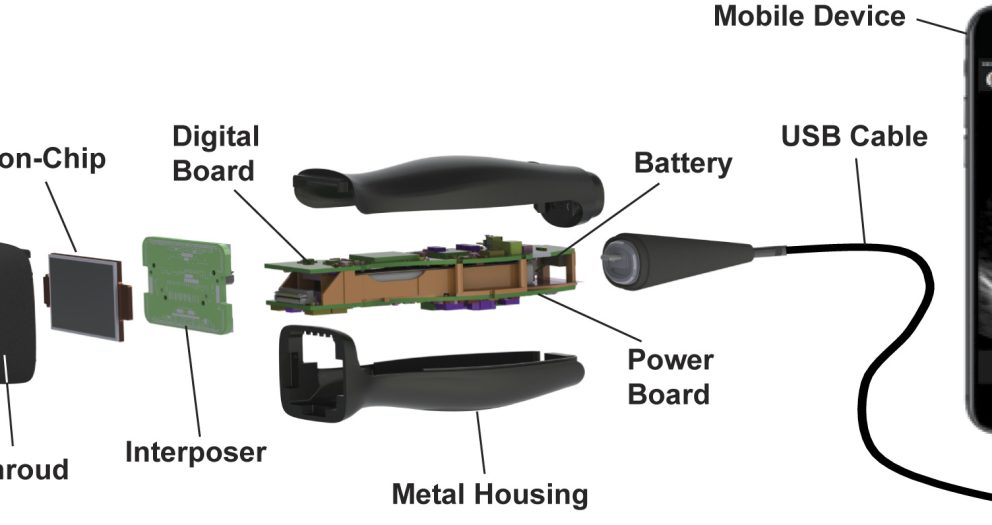
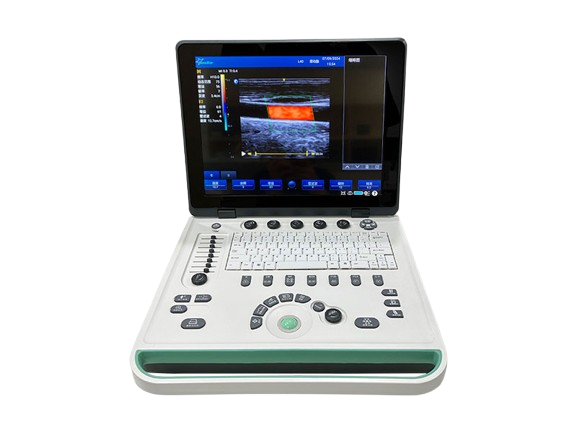
2. Portable Handheld Ultrasound Devices
- Handheld wireless ultrasound devices like the SonoHealth or SonoStar models provide real-time imaging at the bedside or in remote locations, enhancing mobility and diagnostic precision.
3. Wearable Health Tech
- Smartwatches and devices monitor vital signs like heart rate, blood pressure, and blood oxygen levels, enabling remote patient monitoring.
- Example: Apple Watch (ECG and blood oxygen tracking).
4. Telemedicine Platforms
- Video consultation apps and remote care platforms allow doctors to provide care to patients anytime, anywhere.
- Example: Teladoc Health, Doxy.me.
5. Robotic Surgery Systems
- Robotic-assisted systems like Da Vinci Surgery provide precision and minimally invasive procedures with faster recovery times.
6. Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
- Used for medical training, surgical planning, and patient education. VR also helps in pain management and mental health therapy.
- Example: Osso VR for surgical simulations.
7. 3D Printing
- Allows the creation of custom implants, prosthetics, and even organs for transplantation, making treatment personalized and cost-effective.
8. Genomics and Personalized Medicine
- Tools like CRISPR gene editing and DNA sequencing enable targeted therapies based on a patient’s unique genetic makeup.
9. Smart Medical Devices
- Internet of Things (IoT)-enabled devices, such as smart inhalers and connected insulin pens, provide real-time health insights.
10. Blockchain in Healthcare
- Provides secure patient data management, ensuring transparency and trust in medical records.