Biopsy Needle: Comprehensive Guide and Applications
Biopsy needles are indispensable tools in modern medicine, playing a crucial role in the diagnosis of various diseases, particularly cancers. Their ability to extract tissue samples safely and effectively from targeted areas makes them vital for clinical and diagnostic procedures. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the details of biopsy needles, including their types, applications, techniques, benefits, and advancements.
What is a Biopsy Needle?
A biopsy needle is a specialized medical instrument used to obtain tissue samples from the body for microscopic examination and pathological analysis. These samples help clinicians diagnose diseases, determine their severity, and develop appropriate treatment plans. Biopsy needles are designed to minimize patient discomfort while ensuring the accurate collection of tissue from targeted areas.
Applications of Biopsy Needles
Biopsy needles are used in a wide range of medical applications, including:
- Cancer Diagnosis:
- Breast cancer, lung cancer, liver cancer, and prostate cancer are commonly diagnosed using biopsy needles.
- Infectious Diseases:
- Used to analyze tissues affected by infections like tuberculosis or fungal diseases.
- Inflammatory Diseases:
- Assists in diagnosing conditions such as vasculitis, arthritis, and inflammatory bowel diseases.
- Autoimmune Disorders:
- Helps identify disorders like lupus and sarcoidosis by analyzing affected tissues.
- Organ Assessment:
- Liver and kidney biopsies are crucial for diagnosing conditions like hepatitis, cirrhosis, or nephritis.
- Bone and Marrow Analysis:
- Essential for detecting leukemia, lymphoma, and other bone marrow disorders.
Types of Biopsy Needles
Biopsy needles come in various types, each designed for specific applications:
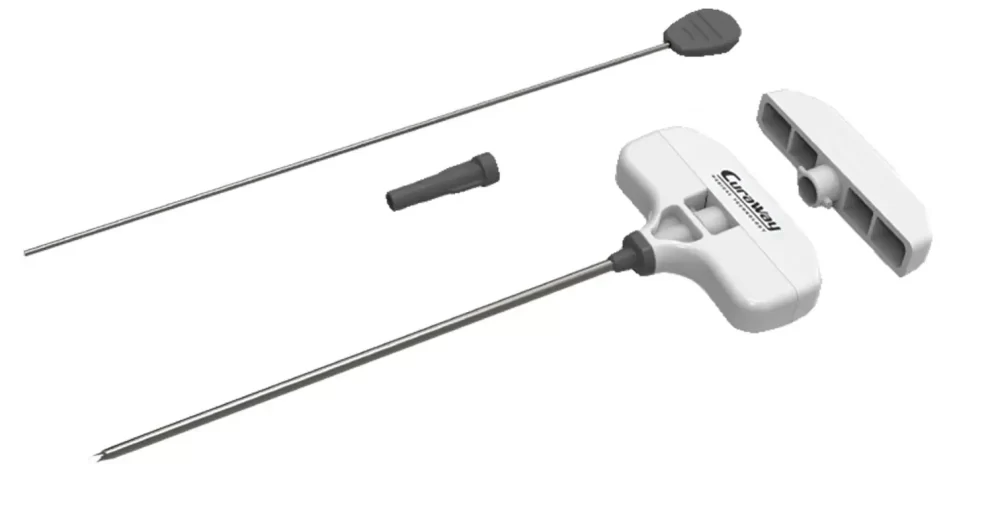
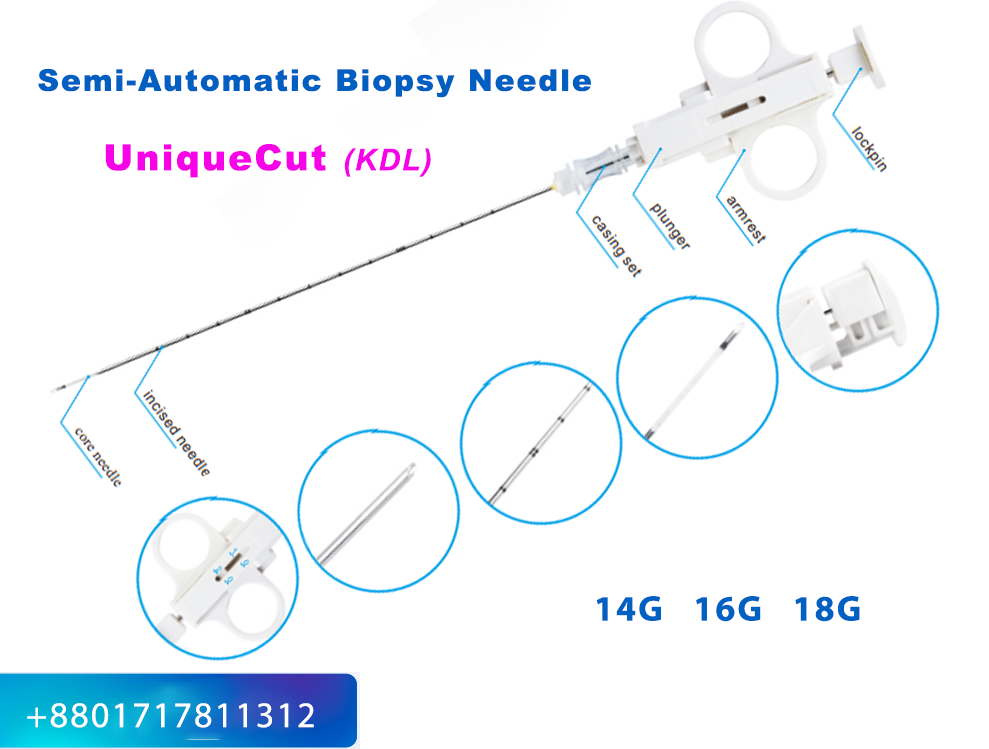
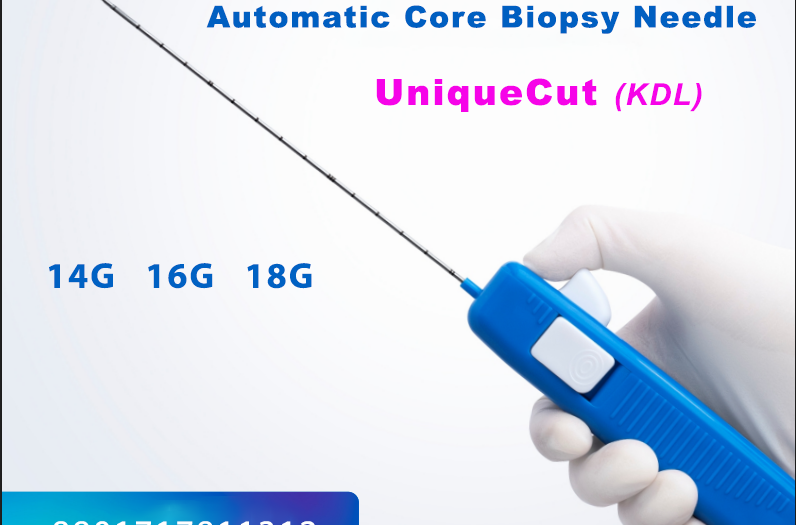
- Core Biopsy Needles:
- These needles extract a cylindrical core of tissue and are used for solid organ biopsies such as breast, prostate, and liver.
- Examples: Tru-Cut needles, spring-loaded needles.
- Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA) Needles:
- Thin needles used to extract cells or fluid for cytological examination.
- Commonly used for thyroid, lymph node, and lung biopsies.
- Vacuum-Assisted Biopsy Needles:
- These use a vacuum mechanism to extract larger tissue samples, often used in breast biopsies.
- Bone Marrow Biopsy Needles:
- Designed to penetrate hard bone and extract marrow tissue for diagnosing blood disorders.
- Punch Biopsy Needles:
- Used primarily for skin biopsies, these needles remove a small circular section of tissue.
- Disposable and Reusable Needles:
- Disposable needles ensure sterility and prevent cross-contamination.
- Reusable needles are cost-effective and often used in low-resource settings.
Key Features of Biopsy Needles
Modern biopsy needles are designed with several features to enhance their performance:
- Echogenic Markings:
- Improve needle visibility during ultrasound-guided procedures.
- Adjustable Lengths and Gauges:
- Available in various lengths and diameters to suit different anatomical targets.
- Biocompatible Materials:
- Constructed from stainless steel or titanium to minimize tissue reaction and ensure durability.
- Sharpened Tips:
- Enable smooth penetration into tissues with minimal trauma.
- User-Friendly Handles:
- Ergonomic designs improve control and precision during procedures.
Guided Biopsy Techniques
Imaging guidance enhances the accuracy and safety of biopsies. Common techniques include:
- Ultrasound-Guided Biopsy:
- Utilizes real-time imaging to precisely target lesions or abnormalities.
- CT-Guided Biopsy:
- Ideal for deep-seated organs like the lungs and abdomen.
- MRI-Guided Biopsy:
- Offers high-resolution imaging for soft tissues such as the brain or breast.
- Fluoroscopy-Guided Biopsy:
- Commonly used for bone biopsies.
- Stereotactic Biopsy:
- Employs a three-dimensional coordinate system, often used in breast cancer diagnostics.
Step-by-Step Biopsy Procedure
The biopsy procedure typically follows these steps:
- Preparation:
- The patient is positioned to allow easy access to the target area.
- Local anesthesia is administered to minimize discomfort.
- Imaging Guidance:
- Imaging techniques are used to locate the lesion or abnormality.
- Needle Insertion:
- The biopsy needle is carefully inserted into the target area.
- Sample Collection:
- Tissue or fluid samples are extracted using the needle.
- Post-Procedure Care:
- The site is cleaned and bandaged, and patients are monitored for any complications.
Advantages of Biopsy Needles
Biopsy needles offer several benefits:
- Minimally Invasive:
- Reduces the need for surgical procedures.
- High Accuracy:
- Provides precise tissue sampling for accurate diagnosis.
- Short Recovery Time:
- Patients can resume normal activities shortly after the procedure.
- Cost-Effective:
- Less expensive compared to surgical biopsy techniques.
- Wide Applicability:
- Suitable for diagnosing a range of diseases and conditions.
Challenges and Risks
While biopsy needles are generally safe, potential challenges include:
- Bleeding:
- Minor bleeding may occur at the biopsy site.
- Infection:
- Rare but possible, especially if sterility is compromised.
- Pain or Discomfort:
- Temporary soreness may occur post-procedure.
- Sampling Errors:
- Inaccurate targeting can lead to inconclusive results.
Advancements in Biopsy Needle Technology
The medical field has witnessed significant advancements in biopsy needle technology:
- Smart Needles:
- Equipped with sensors for real-time feedback on tissue density and needle placement.
- Robotic-Assisted Biopsies:
- Enhance precision and reduce operator fatigue.
- AI-Guided Systems:
- Use artificial intelligence to identify optimal biopsy sites.
- 3D Imaging Integration:
- Combines multiple imaging modalities for improved accuracy.
- Echogenic Coatings:
- Further enhance needle visibility under ultrasound.
Biopsy Needles in Bangladesh
In Bangladesh, biopsy needles are gaining widespread use in hospitals, diagnostic centers, and specialized clinics. Companies like UniqueCut (KDL) and Unique Medi Trade are at the forefront of introducing advanced biopsy needle systems in the country. Their collaboration ensures that Bangladeshi healthcare professionals have access to world-class tools and technologies for diagnostics and treatment planning.
Future of Biopsy Needles
The future of biopsy needles looks promising, with ongoing research focused on:
- Nanotechnology Integration:
- Developing ultra-thin needles for less invasive procedures.
- Personalized Medicine:
- Designing needles tailored to individual patient needs.
- Automation:
- Fully automated biopsy systems for improved efficiency.
- Sustainability:
- Eco-friendly materials for disposable needles.
- Enhanced Patient Comfort:
- Minimizing pain and anxiety during procedures.
Conclusion
Biopsy needles are transformative tools in modern medicine, providing invaluable support for diagnosing and managing diseases. With continued advancements in technology and widespread adoption across healthcare systems, biopsy needles are set to remain at the forefront of diagnostic innovations. As global and local partnerships expand, their accessibility and effectiveness will continue to improve, benefiting patients worldwide.
 Contact
Contact
Unique Medi Trade