Importance of Handheld Ultrasound for Nerve Block in Anesthesiologists
Handheld ultrasound is an innovative technology that has transformed the field of anesthesia, particularly for nerve block procedures. Here are 10 key points highlighting the importance of handheld ultrasound for nerve block in anesthesia:
- Handheld ultrasound devices are portable and lightweight, allowing for convenient and easy use in clinical settings, including operating rooms, clinics, and emergency departments.
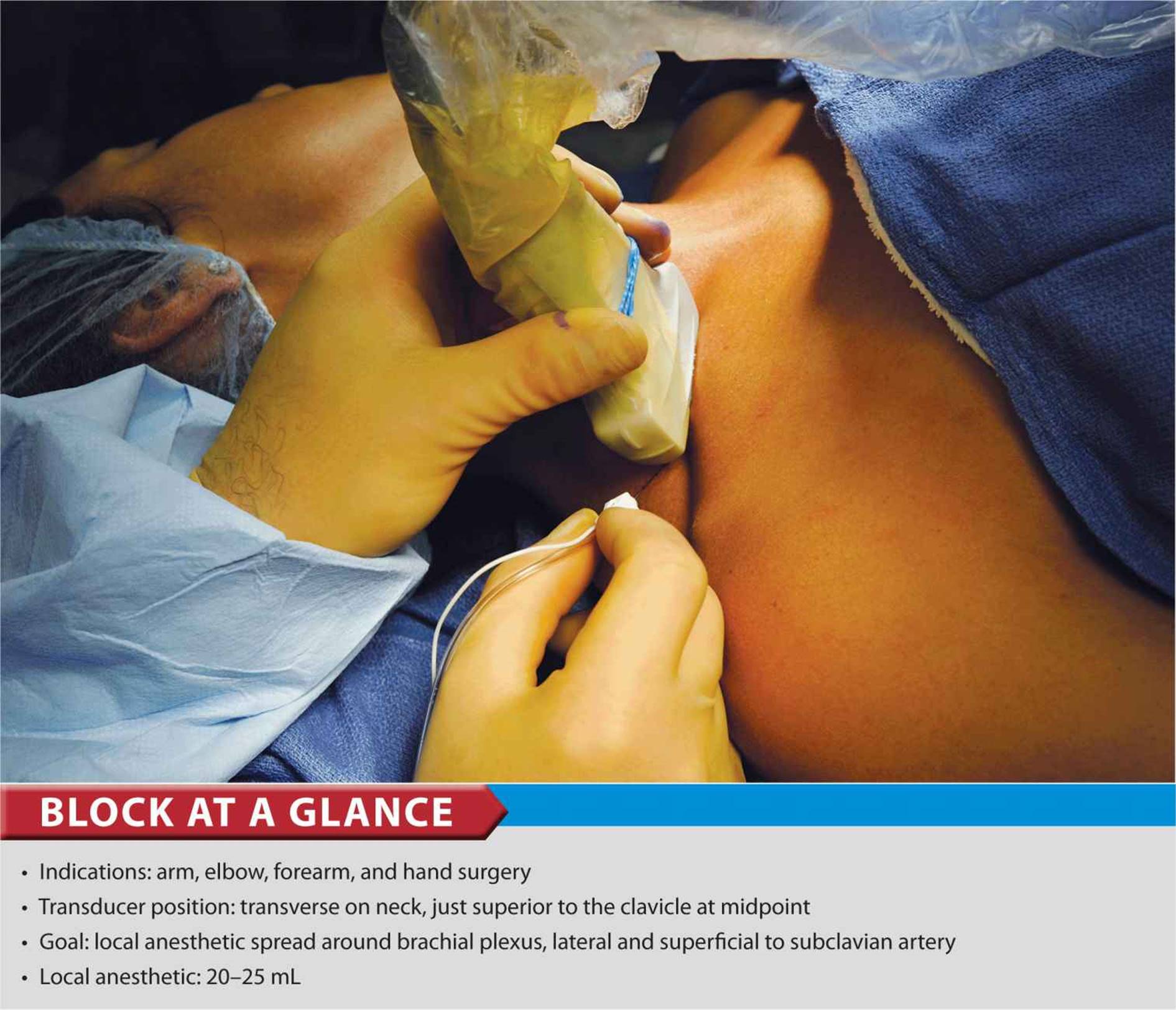
- Ultrasound guidance enhances the accuracy and safety of nerve block procedures by providing real-time visualization of the needle tip and surrounding anatomy, reducing the risk of complications such as nerve damage, bleeding, and infection.
- Compared to traditional techniques such as nerve stimulation and landmark-based methods, ultrasound-guided nerve blocks offer superior visualization, faster onset, and longer-lasting analgesia, resulting in improved patient outcomes.
- Handheld ultrasound devices allow anesthesiologists to perform nerve blocks in difficult-to-access areas, such as the neck, back, and extremities, with greater precision and confidence, leading to more successful outcomes and fewer complications.
- Ultrasound-guided nerve blocks are particularly useful for patients who are unable to tolerate general anesthesia, have contraindications to opioids, or require postoperative pain control for extended periods.
- Handheld ultrasound devices are cost-effective and can potentially reduce healthcare costs by reducing the need for additional imaging and surgical procedures.
- The use of handheld ultrasound for nerve blocks has been shown to reduce the length of hospital stays and improve patient satisfaction, leading to better overall patient outcomes.
- Ultrasound-guided nerve blocks can be used for a variety of procedures, including upper and lower extremity blocks, truncal blocks, and neuraxial blocks, making them a versatile and valuable tool for anesthesiologists.
- The use of handheld ultrasound devices for nerve blocks is rapidly expanding and is becoming a standard of care in many medical institutions around the world.
- Training in the use of handheld ultrasound devices for nerve blocks is readily available, and continuing education and proficiency in the technique are important for anesthesiologists who wish to provide the highest level of care to their patients.