Modern medical science is a vast and rapidly evolving field that integrates technology, biology, chemistry, and other scientific disciplines to prevent, diagnose, and treat diseases while improving the overall health and well-being of individuals and communities. Below are some key areas shaping modern medical science:
1. Diagnostic Advancements
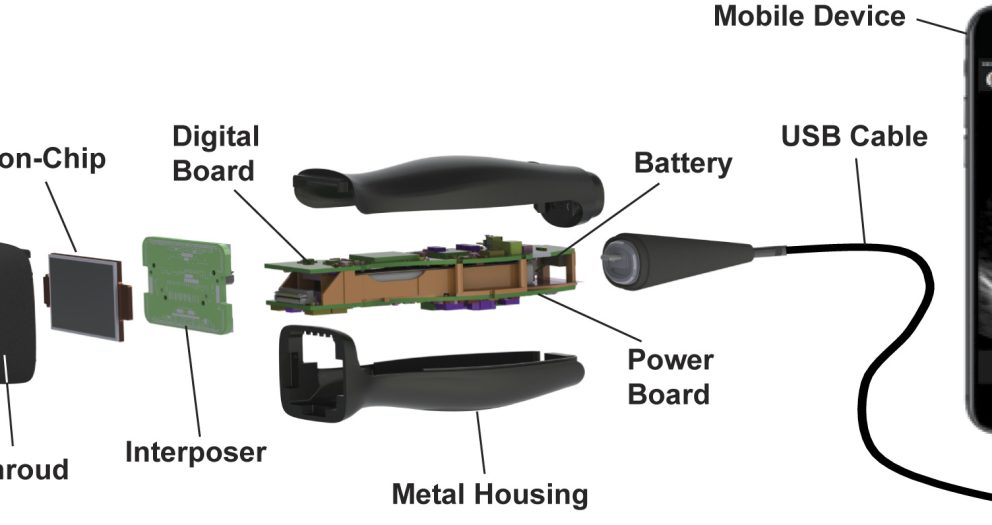
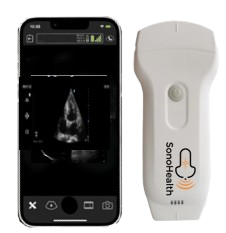
- Imaging Technologies: Innovations such as Handheld Wireless Portable Ultrasound devices, AI-enhanced CT/MRI scans, and PET imaging provide early and accurate disease diagnosis.
- Genomics: DNA sequencing and personalized medicine allow for precise diagnosis and targeted therapies based on a person’s genetic makeup.
- Point-of-Care Testing (POCT): Handheld devices enable quick and accurate testing outside traditional labs, aiding immediate decision-making.
2. Treatment Innovations
- Regenerative Medicine: Stem cell therapy and tissue engineering are opening doors to treating previously incurable conditions.
- Biologics and Biosimilars: Advanced drugs derived from living organisms are used for autoimmune diseases, cancer, and more.
- Minimally Invasive Surgery: Techniques like robotic-assisted surgery and laparoscopy reduce recovery time and complications.
3. Digital Health and AI
- Wearables: Smart devices monitor vital signs in real-time, helping manage chronic diseases like diabetes and hypertension.
- AI in Medicine: Machine learning assists in diagnosing diseases, predicting outcomes, and optimizing treatment plans.
- Telemedicine: Remote consultations make healthcare accessible, especially in underserved areas.
4. Public Health and Epidemiology
- Vaccination: New vaccines, such as mRNA-based ones for COVID-19, are improving pandemic preparedness.
- Global Health Initiatives: Collaborative efforts combat diseases like malaria, TB, and HIV.
5. Ethical and Regulatory Developments
- CRISPR and Gene Editing: Ethical considerations are rising alongside technologies that can alter human DNA.
- Data Privacy: With digital records and AI, maintaining patient confidentiality is a critical concern.
6. Integration of Emerging Technologies
- 3D Printing: Producing custom prosthetics, implants, and even organs.
- Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology for targeted drug delivery and early disease detection.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): Used for surgical training and rehabilitation therapy.
Impact on Society
Modern medical science significantly extends life expectancy, improves quality of life, and reduces the burden of diseases. However, challenges like equitable access, affordability, and ethical dilemmas remain at the forefront of discussions.