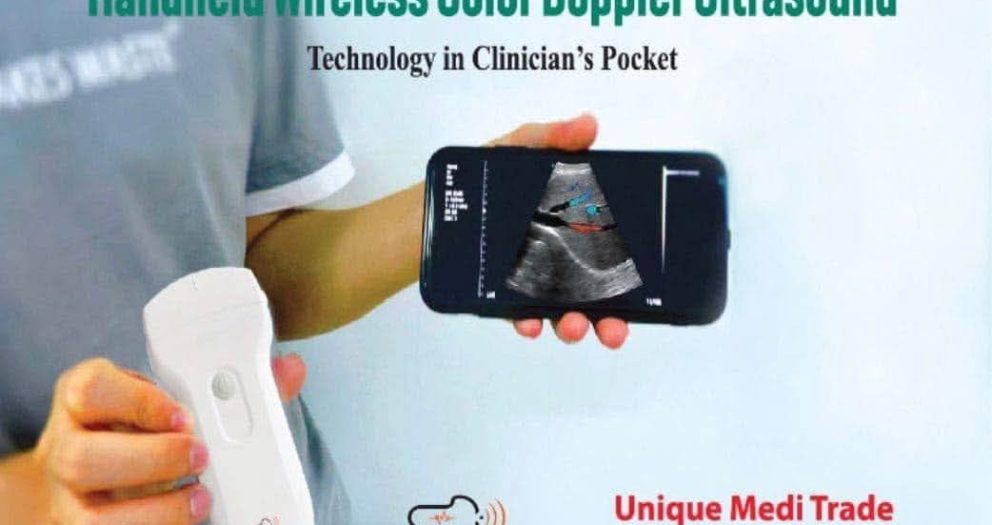
Handheld Wireless Pocket Ultrasound
Revolutionize Your Medical Diagnostics with Handheld Wireless Color Doppler Ultrasound
Experience the next level of medical imaging with our handheld wireless color Doppler ultrasound devices designed for modern healthcare professionals. Whether you're in a clinical setting, on a home visit, or working in emergency care, these portable solutions empower you to perform quick, accurate, and real-time diagnostics with ease.
🔍 Key Features:
- Multiple probes (Convex, Linear, and Phased) for versatile applications
- Color Doppler technology for detailed vascular imaging
- Wireless and lightweight for maximum portability
- Compatible with smartphones and tablets for instant visualization
- US FDA, CE, and ISO certified for reliability and safety
Ideal for vascular medicine, general diagnostics, and point-of-care applications, this innovative tool brings advanced imaging right to your pocket.
🟦 1. Handheld Wireless Color Doppler Ultrasound
The handheld wireless color Doppler ultrasound is transforming medical imaging by offering real-time diagnostic power in a compact, mobile form. This technology allows healthcare professionals to perform advanced imaging at the point of care without the need for bulky, stationary ultrasound machines.
Equipped with color Doppler capabilities, it provides detailed blood flow visualization, making it ideal for vascular assessments, cardiac evaluations, and deep organ analysis. The wireless connectivity enables seamless integration with smartphones and tablets, allowing for instant display, sharing, and storage of images.
The greatest advantage is its portability. Doctors can carry this device during emergency rounds, outpatient consultations, or even in remote rural locations. This improves the speed of diagnosis and patient outcomes, especially in time-sensitive cases.
Moreover, these devices are typically compatible with multiple probe types—convex, linear, and phased array—making them versatile tools for OB-GYN, cardiology, internal medicine, and primary care. With regulatory approvals such as FDA and CE certifications, handheld wireless Doppler ultrasound devices are safe, accurate, and increasingly popular in modern clinical practice.
Whether you’re a clinician looking to upgrade your diagnostic tools or a hospital administrator aiming to improve your imaging capacity, the handheld wireless color Doppler ultrasound offers the perfect balance of convenience, precision, and performance.
🟦 2. Handheld Ultrasound Device
A handheld ultrasound device is a compact, portable imaging solution designed for point-of-care diagnostics. It offers the same essential imaging capabilities as traditional ultrasound systems but in a much smaller and more user-friendly format.
These devices are especially popular among emergency physicians, intensivists, and general practitioners who require rapid, bedside evaluation tools. With integrated probes and real-time imaging, they are capable of providing crucial insights into cardiac function, abdominal organs, musculoskeletal issues, and more.
One of the main advantages of handheld ultrasound devices is mobility. Physicians can carry them in their coat pocket or medical bag, making them ideal for home visits, emergency services, and rural outreach. The integration with smartphones or tablets means that images can be viewed immediately and saved securely to the cloud or shared with specialists for quick consultations.
Many handheld ultrasound devices also feature color Doppler functionality, enabling the visualization of blood flow and vascular conditions. This enhances their utility in diagnosing DVT, arterial occlusion, and cardiac abnormalities.
Modern handheld ultrasound devices are designed with AI assistance, automatic measurements, and preset modes to support faster learning curves and more accurate results. These tools are revolutionizing how clinicians approach bedside diagnostics, making healthcare faster, more accessible, and more patient-centered.
🟦 3. Wireless Ultrasound Machine
A wireless ultrasound machine represents a breakthrough in medical imaging technology, removing the constraints of cables and heavy equipment. These machines connect wirelessly to smartphones, tablets, or laptops, providing instant access to high-quality ultrasound imaging anywhere, anytime.
The wireless nature enhances the portability and ease of use, especially in dynamic environments like emergency rooms, ambulances, or even during field missions. Wireless ultrasound machines support various probes, such as linear, convex, and phased array, and many models combine them into a single 3-in-1 device.
With color Doppler features, these machines are suitable for vascular analysis, fetal monitoring, soft tissue examination, and cardiac diagnostics. The lack of cables reduces the risk of contamination and simplifies the cleaning process, which is crucial in sterile settings such as operating rooms or ICUs.
Battery-powered and compact, a wireless ultrasound machine can operate for hours and recharge quickly. Image quality in modern devices often matches traditional systems, with some offering HD or 3D visualization. Most are equipped with intuitive mobile apps that allow image annotation, cloud storage, and real-time telemedicine sharing.
For clinicians who need quick, accurate diagnostics on the move, wireless ultrasound machines are an indispensable part of today’s healthcare technology landscape. They empower better decision-making and enhance patient care, particularly in under-resourced or time-critical scenarios.
🟦 4. Portable Doppler Ultrasound
Portable Doppler ultrasound devices have changed how clinicians evaluate blood flow, vascular conditions, and organ perfusion. These compact tools use Doppler technology to detect and measure the movement of blood through vessels, making them essential for cardiologists, vascular surgeons, and emergency medicine providers.
Unlike traditional Doppler machines, portable versions are lightweight, easy to carry, and suitable for point-of-care use. They often feature color Doppler imaging, which enhances visibility and allows clinicians to identify blockages, stenosis, or abnormal blood flow patterns instantly.
These devices are especially useful in critical care units, ambulances, and home-based medical services. With real-time imaging and wireless data sharing, doctors can quickly assess patients and make informed decisions without waiting for access to a full radiology suite.
Modern portable Doppler ultrasounds are built with AI features, touch-screen controls, and automated measurements. Many can store reports digitally and export findings directly to electronic health records. Additionally, they are increasingly integrated into telemedicine platforms, making remote diagnostics more effective.
In resource-limited settings or fast-paced environments, a portable Doppler ultrasound becomes a lifesaving tool, ensuring that vascular complications are detected and treated promptly.
🟦 5. Handheld USG Machine
A handheld USG machine is a powerful innovation in diagnostic imaging that brings hospital-grade ultrasound technology into a compact, mobile device. “USG” refers to ultrasonography, and these devices allow clinicians to perform various types of scans directly at the patient’s bedside or in the field.
Unlike bulky, cart-based systems, handheld USG machines are small enough to fit in a pocket. They are ideal for rapid examinations in emergency departments, ambulances, or outpatient clinics. Despite their size, they offer high-resolution imaging and advanced features such as color Doppler, M-mode, and AI-assisted scanning.
These machines are often compatible with Android and iOS devices, allowing users to visualize scans on their phones or tablets. They support multiple probes—convex for abdominal scans, linear for vascular imaging, and phased array for cardiac assessments—all integrated into a single wireless device.
One of the biggest benefits of handheld USG machines is their affordability and accessibility. They make ultrasound technology more available to rural doctors, mobile health workers, and underfunded clinics. With cloud storage and remote consultation features, they are also perfect for telehealth applications.
Whether you’re monitoring fetal health, evaluating trauma injuries, or performing quick vascular checks, a handheld USG machine offers speed, accuracy, and convenience in one compact package.
🟦 6. Portable Ultrasound Scanner
A portable ultrasound scanner is a compact and efficient diagnostic tool used to visualize organs, tissues, and blood flow in real-time. These scanners have revolutionized point-of-care medicine, enabling clinicians to perform fast and accurate assessments directly at the patient’s bedside.
Ideal for emergency medicine, ICU, ambulances, and remote clinics, portable ultrasound scanners often support multiple probe types—linear, convex, or phased array—for versatility in scanning different body parts. The inclusion of Doppler technology further enhances their value by enabling blood flow analysis, crucial for vascular assessments and cardiac evaluations.
Modern portable ultrasound scanners are often wireless and connect to smartphones or tablets. This allows doctors to view high-resolution images instantly, store patient data securely, and even share findings remotely for teleconsultations. Many models now come equipped with AI features, automatic measurements, and user-friendly interfaces, making them suitable even for non-radiology specialists.
Portable ultrasound scanners are lightweight, rechargeable, and highly durable. Some can operate continuously for hours and offer waterproof and dustproof protection, making them perfect for field hospitals and disaster relief zones.
As healthcare moves toward more personalized and rapid diagnostics, the portable ultrasound scanner is an indispensable tool. It empowers medical professionals to make informed decisions faster, enhances patient satisfaction, and improves healthcare outcomes in both urban and rural settings.
🟦 7. Wireless USG Device
The wireless USG (ultrasonography) device is an innovation that redefines mobility in medical imaging. With no cables or bulky machines, this device connects wirelessly to tablets, smartphones, or computers, offering instant ultrasound imaging in a wide variety of clinical settings.
Wireless USG devices are particularly valuable in emergency care, rural health centers, telemedicine, and mobile healthcare services. They come in compact, handheld formats and often support multiple scanning modes including B-mode, M-mode, and color Doppler for visualizing organ structure and blood flow.
One of the key benefits of a wireless USG device is flexibility. Healthcare providers can use the same device across departments, from OB-GYN to internal medicine, pediatrics, and cardiology. This improves resource utilization while reducing equipment costs. The lack of wires also means less contamination risk in sterile environments like operating rooms and ICUs.
Many wireless USG devices are powered by advanced AI, allowing automatic measurements and guided scanning protocols. This shortens the learning curve for new users and ensures consistency across operators.
Ideal for point-of-care use, a wireless USG device enables faster diagnosis, quicker interventions, and better patient outcomes. It's an essential tool for modern, efficient, and patient-focused healthcare delivery.
🟦 8. Point of Care Ultrasound (POCUS)
Point of Care Ultrasound (POCUS) refers to the use of portable ultrasound devices at a patient’s bedside to make immediate clinical decisions. Unlike traditional ultrasound, which is often done in radiology departments, POCUS empowers frontline healthcare providers to perform diagnostic imaging in real-time.
POCUS is commonly used in emergency rooms, intensive care units, and primary care settings. It enables clinicians to assess cardiac activity, detect fluid accumulation, evaluate lung pathology, and guide needle placements quickly and accurately. With color Doppler integration, it becomes even more powerful, allowing blood flow assessments and vascular evaluations.
Handheld POCUS devices are compact, wireless, and often compatible with smartphones or tablets. This allows for rapid deployment in critical scenarios like trauma, cardiac arrest, or labor complications. These devices reduce patient wait times, eliminate unnecessary referrals, and enhance clinical efficiency.
Recent advancements include AI-powered image enhancement, auto-calibration, and cloud-based data storage. These features make POCUS more accessible, even to non-specialists, while maintaining diagnostic accuracy.
POCUS represents a significant leap toward patient-centered care. It enables faster diagnoses, minimizes delays, and improves clinical outcomes. As technology advances, POCUS is poised to become a standard tool across all medical disciplines.
🟦 9. 3-in-1 Ultrasound Probe
The 3-in-1 ultrasound probe combines convex, linear, and phased array transducers into a single compact device, offering unmatched versatility for point-of-care ultrasound. It enables clinicians to perform a wide range of scans—from abdominal and cardiac to vascular and musculoskeletal—without switching probes.
This type of probe is particularly useful in fast-paced environments like emergency rooms, ambulances, and rural clinics. With just one handheld device, healthcare providers can assess a trauma patient’s abdomen, evaluate cardiac function, and scan for DVT all within minutes.
The 3-in-1 ultrasound probe is often wireless, compatible with iOS and Android devices, and provides high-resolution imaging with color Doppler functionality. This allows for detailed visualization of blood flow, organ structures, and pathology detection in real-time.
Its compact design and long battery life make it an excellent option for mobile healthcare providers, telemedicine services, and outreach programs. Additionally, AI support and preset imaging modes enhance usability, especially for non-radiology professionals.
By integrating multiple scanning modes into one device, the 3-in-1 ultrasound probe significantly reduces equipment costs, enhances portability, and simplifies training and usage. It’s the future of accessible and efficient diagnostic imaging.
🟦 10. Color Doppler Ultrasound Machine
A color Doppler ultrasound machine is a medical imaging tool that visualizes blood flow within the body using sound waves. By assigning color to different flow directions and velocities, it helps clinicians detect abnormalities such as clots, blockages, or turbulent flow patterns.
These machines are invaluable in cardiology, obstetrics, nephrology, and vascular medicine. They allow the evaluation of fetal blood flow, carotid artery patency, renal artery perfusion, and heart valve performance. In trauma care, they help identify internal bleeding or vascular injury quickly.
Traditional color Doppler machines were large and stationary. However, modern versions are increasingly portable and even wireless. Handheld color Doppler ultrasound devices offer the same core capabilities in a compact format, perfect for bedside assessments and emergency situations.
Advanced machines now come with features like pulse wave Doppler, power Doppler, and real-time image sharing. Integration with mobile apps and cloud platforms makes it easy to store, review, and share reports with specialists or patients.
For any clinical setting focused on speed, precision, and mobility, a color Doppler ultrasound machine is a must-have. It’s a critical asset for improving diagnostics and enhancing patient care outcomes.
🟦 11. Handheld Color Doppler Ultrasound
A handheld color Doppler ultrasound is a revolutionary device that combines portability with powerful imaging features, making it ideal for bedside diagnostics and point-of-care use. It enables real-time visualization of tissue structures and blood flow using color-coded Doppler imaging.
Traditionally, Doppler ultrasound was limited to bulky machines in radiology departments. Today, with the advent of handheld solutions, clinicians in emergency rooms, outpatient clinics, ambulances, and even home care settings can perform vascular assessments and detect abnormalities quickly.
The handheld color Doppler ultrasound typically connects wirelessly to smartphones or tablets via dedicated apps. These devices support multiple imaging modes such as B-mode, Color Doppler, and Pulse Wave Doppler, offering diagnostic versatility in a single compact unit.
Medical professionals in cardiology, OB-GYN, internal medicine, and critical care find this tool essential for scanning the heart, veins, arteries, and organs without delays. Its real-time results reduce referral wait times and improve decision-making speed during acute patient care.
Most devices feature high-resolution imaging, built-in AI algorithms for guidance, and rechargeable batteries that support hours of continuous scanning. As such, handheld color Doppler ultrasound is rapidly becoming a standard tool in modern, efficient healthcare delivery systems.
🟦 12. Wireless Doppler Ultrasound
Wireless Doppler ultrasound offers a groundbreaking advancement in medical imaging by eliminating cables and allowing freedom of movement during examinations. This device uses Doppler technology to evaluate blood flow through vessels and the heart while wirelessly transmitting the images to a connected mobile device or tablet.
This is especially useful in environments where mobility is essential, such as ICUs, ambulances, rural clinics, and during surgical procedures. The absence of wires reduces infection risks and enhances convenience for both clinicians and patients.
Wireless Doppler ultrasound devices typically include color Doppler, power Doppler, and pulse wave Doppler capabilities. These modes allow accurate detection of blood clots, vascular abnormalities, fetal circulation issues, and cardiac conditions.
Another benefit is compatibility across platforms—most devices work seamlessly with iOS, Android, and Windows systems. Their intuitive apps often include real-time recording, report generation, and cloud storage features for easy sharing and backup.
Lightweight, rechargeable, and highly durable, these devices can operate for several hours on a single charge and are often water-resistant. Whether for emergency assessments, remote healthcare, or telemedicine, wireless Doppler ultrasound systems redefine accessibility and precision in diagnostics.
🟦 13. Portable Color Doppler Ultrasound
Portable color Doppler ultrasound systems offer a versatile and compact solution for high-quality imaging and blood flow analysis at the point of care. These devices provide color-coded visualization of blood circulation, helping healthcare providers assess cardiovascular conditions, organ perfusion, and fetal well-being efficiently.
Unlike traditional bulky systems, portable models are designed to be lightweight and easy to transport. Whether in field hospitals, rural clinics, emergency departments, or outpatient care, their mobility ensures prompt diagnostics and reduces patient transfer delays.
These systems support key imaging modes—B-mode, Color Doppler, and Power Doppler—with many models offering advanced options like Tissue Harmonic Imaging and 3D rendering. They’re ideal for scanning the abdomen, heart, thyroid, vessels, and musculoskeletal structures.
Modern portable color Doppler ultrasound devices often feature touchscreens, wireless connectivity, and compatibility with mobile applications. AI-driven measurement tools further improve accuracy and reduce operator dependence.
Their affordability, ease of use, and diagnostic capabilities make them suitable for both general practitioners and specialists. In short, portable color Doppler ultrasound is a transformative solution that brings accurate imaging to any setting, improving care quality and patient satisfaction.
🟦 14. Best Handheld Ultrasound Machine
Choosing the best handheld ultrasound machine involves evaluating performance, versatility, image quality, and user-friendliness. These compact devices are changing the face of diagnostic imaging by allowing clinicians to conduct real-time scans wherever needed—hospital rooms, clinics, or even in the field.
The best handheld ultrasound machines combine multiple scanning modes (B-mode, M-mode, Color Doppler) with AI-enhanced imaging. Some even offer 3-in-1 probes (Convex, Linear, and Phased Array) in a single unit, reducing the need for multiple devices.
High-resolution imaging is a priority, along with fast boot times, responsive touch interfaces, and wireless connectivity to smartphones or tablets. A good device should support iOS, Android, and Windows systems, with secure data sharing, DICOM compatibility, and cloud storage for easy reporting.
Battery life, durability, and sterilization compatibility are also crucial, especially in high-pressure or remote environments. Whether you’re a cardiologist, internist, or emergency physician, the right handheld ultrasound device enhances diagnostic speed and confidence.
Overall, the best handheld ultrasound machines are those that deliver hospital-grade performance in your pocket, revolutionizing patient care at every level.
🟦 15. Wireless Ultrasound Device for Vascular Access
A wireless ultrasound device for vascular access offers clinicians real-time guidance for locating veins and arteries, significantly improving the safety and success rate of procedures such as IV cannulation, central line placement, and dialysis access.
These devices are particularly beneficial in critical care, emergency medicine, and anesthesia. With color Doppler functionality, clinicians can assess vessel patency and identify arteries or veins, even in patients with difficult anatomy or low blood pressure.
Unlike traditional ultrasound machines, wireless models are compact, easy to sterilize, and highly mobile. They connect to smartphones or tablets, displaying live imaging that enhances hand-eye coordination during vascular procedures.
The integration of AI-based guidance systems can further assist in identifying optimal puncture sites, ensuring consistency across users. This is especially useful for medical students, residents, or nurses undergoing ultrasound training.
Waterproof casings, long battery life, and minimal setup time make these devices ideal for both hospital and prehospital settings. A wireless ultrasound device for vascular access not only increases procedure efficiency but also reduces complications and enhances patient comfort.
🟦 16. Handheld Ultrasound Scanner
A handheld ultrasound scanner is a game-changing device in modern medical imaging, offering portability, precision, and real-time diagnostics in the palm of your hand. This compact device connects to smartphones, tablets, or laptops and is widely used in hospitals, clinics, and remote areas.
The scanner is ideal for point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS), enabling rapid assessments at the bedside. Whether you’re checking cardiac function, performing abdominal scans, or assessing fetal growth, a handheld ultrasound scanner delivers fast and accurate results without needing bulky equipment.
Most modern handheld ultrasound scanners come with high-resolution probes and support multiple modes like B-mode, Color Doppler, and Pulse Wave Doppler. These features help in evaluating both anatomical structures and blood flow, especially in emergency and critical care scenarios.
Wireless functionality allows seamless data sharing and cloud storage for patient records. Battery-powered and easy to sterilize, these scanners are perfect for high-turnover environments like ERs, ambulances, and disaster zones.
The affordability and ease of use make the handheld ultrasound scanner a must-have for general practitioners, specialists, and telemedicine providers looking to enhance diagnostic speed and accuracy.
🟦 17. Wireless Portable Ultrasound Scanner
The wireless portable ultrasound scanner is transforming how healthcare professionals perform diagnostic imaging. This cordless, pocket-sized device enables clinicians to perform high-quality ultrasound exams anywhere—at the bedside, in the ambulance, or during home visits.
Unlike traditional systems, this scanner connects wirelessly to smartphones and tablets via apps, displaying clear, real-time images. It supports B-mode and color Doppler imaging, making it ideal for examining organs, soft tissues, vessels, and even fetal development.
Because it is wireless and portable, it's especially useful for emergency care, remote healthcare, rural clinics, and mobile health services. Its compact design allows quick sterilization and easy handling during sterile procedures.
The wireless portable ultrasound scanner often includes rechargeable batteries that provide hours of operation, AI-guided imaging, and data archiving features. Many models are compatible with both iOS and Android systems.
Overall, this device is revolutionizing access to ultrasound diagnostics, improving workflow efficiency, and ensuring timely patient care across a variety of medical fields.
🟦 18. Pocket-Sized Ultrasound Machine
A pocket-sized ultrasound machine brings hospital-grade imaging to your fingertips. These ultra-compact devices are small enough to fit in your coat pocket yet powerful enough to produce high-resolution images for clinical decision-making.
Used in fields like emergency medicine, internal medicine, OB-GYN, and anesthesiology, these machines support B-mode, color Doppler, and spectral Doppler functions. Physicians can scan the heart, lungs, abdomen, blood vessels, and musculoskeletal system with speed and precision.
Pocket-sized ultrasound machines are typically wireless and connect to smartphones or tablets via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi. They come with intuitive apps that allow for easy scanning, report creation, and secure data sharing.
These devices are ideal for use in resource-limited settings, field hospitals, and mobile healthcare units. They help reduce diagnostic delays, minimize patient transfers, and lower healthcare costs.
Whether you’re a medical student or a senior clinician, a pocket-sized ultrasound machine enhances diagnostic capabilities wherever and whenever needed—making it an indispensable tool in modern medical practice.
🟦 19. Handheld Doppler Ultrasound for Cardiac Imaging
A handheld Doppler ultrasound for cardiac imaging is a crucial tool for evaluating heart function and blood flow in real-time. This portable device uses Doppler technology to detect and measure the movement of blood through the heart’s chambers and valves.
Traditionally, cardiac imaging required large echocardiography machines. Now, with handheld Doppler ultrasounds, physicians can conduct fast, bedside heart assessments in clinics, emergency rooms, or even during house calls.
These devices support both Color Doppler and Pulsed Wave Doppler modes, which are essential for detecting valve disorders, heart murmurs, and heart failure. Many models also feature ECG synchronization and AI assistance for improved diagnostic accuracy.
The compact design allows easy transport, while wireless connectivity provides instant display and sharing of images on mobile devices. With rechargeable batteries and robust construction, this device is suitable for continuous use in critical care, cardiology, and primary care.
A handheld Doppler ultrasound for cardiac imaging is a life-saving innovation, delivering quick insights that can significantly influence treatment outcomes.
🟦 20. Handheld Ultrasound Probe
The handheld ultrasound probe is the core component of compact imaging systems, offering powerful scanning capabilities in a small, user-friendly format. It’s a vital tool in today’s point-of-care and bedside diagnostic practices.
Unlike traditional probes attached to large machines, handheld ultrasound probes are built to connect wirelessly with tablets or smartphones. These probes can support multiple frequencies and scanning modes such as B-mode, Color Doppler, and even 3D imaging, depending on the model.
Available in Convex, Linear, and Phased Array variants—or as 3-in-1 multihead models—they are versatile enough to scan everything from deep abdominal organs to superficial blood vessels and musculoskeletal structures.
Handheld probes are ideal for fast diagnostics, especially in emergency, ICU, surgical, and outpatient settings. Their portability and ease of sterilization also make them suitable for use in sterile fields.
With cloud storage, AI-driven analysis, and compatibility with mobile platforms, handheld ultrasound probes are modernizing clinical workflows and delivering better outcomes through faster, more accessible imaging.
🟦 21. Wireless Handheld Ultrasound Scanner
A wireless handheld ultrasound scanner is transforming point-of-care diagnostics by offering mobility, accuracy, and real-time imaging—all without cables or bulky equipment. This compact device connects wirelessly to smartphones or tablets and is widely used across emergency rooms, ICU, outpatient clinics, and even in rural areas.
Equipped with advanced imaging modes like B-mode, Color Doppler, and Pulsed Wave Doppler, it enables physicians to evaluate internal organs, vessels, and fetal health instantly. The scanner’s portability means healthcare professionals can carry it in their pocket and perform bedside scans within seconds.
Designed for efficiency, many wireless handheld ultrasound scanners come with rechargeable batteries, waterproof probes, and intuitive mobile apps that support image storage, sharing, and AI-assisted diagnosis. Whether it’s for cardiac assessments, abdominal scans, or musculoskeletal imaging, this device delivers high-quality images on demand.
Its wireless capability enhances workflow, reduces clutter, and increases access to diagnostic imaging in underserved areas. This innovation is revolutionizing ultrasound usage by putting diagnostic power directly into the hands of clinicians—anytime, anywhere.
🟦 22. Handheld Ultrasound Machine Price
When considering a handheld ultrasound machine, price is often a key factor for clinics, hospitals, and individual practitioners. These compact and wireless devices offer a cost-effective alternative to traditional ultrasound systems while delivering comparable image quality and functionality.
The price of a handheld ultrasound machine varies depending on features, probe type, brand, and region. Entry-level models may start at $2,000–$3,000, while more advanced devices with color Doppler, 3-in-1 probes, and AI support can range from $4,000 to $8,000 or more.
Despite the investment, handheld ultrasound machines reduce long-term costs by cutting down on patient transfers, expediting diagnostics, and lowering equipment maintenance fees. Many models are compatible with smartphones or tablets, eliminating the need for an expensive console.
These machines are widely used in emergency medicine, internal medicine, OB-GYN, and even in veterinary practices. When evaluating price, consider build quality, warranty, support, and software updates—all of which add value over time.
In summary, a handheld ultrasound machine offers significant returns on investment through mobility, speed, and diagnostic accuracy, making it an ideal solution for modern healthcare settings.
🟦 23. Best Handheld Ultrasound Machine
Choosing the best handheld ultrasound machine involves evaluating several factors: image quality, portability, probe versatility, software support, and affordability. Today’s best handheld devices rival traditional cart-based systems and provide real-time diagnostics in a compact format.
The top-performing handheld ultrasound machines feature multiple imaging modes including B-mode, Color Doppler, PW Doppler, and M-mode. Some even offer 3-in-1 probes (Convex, Linear, Phased Array) or AI-guided scanning for more accurate and quicker evaluations.
Leading brands such as SonoStar, Konted, Butterfly iQ, and Clarius are known for their exceptional image resolution, wireless connectivity, and mobile app integration. These devices often connect seamlessly with iOS and Android platforms, enabling image sharing, reporting, and cloud storage.
The best handheld ultrasound machines are used in emergency medicine, internal medicine, ICU, gynecology, and point-of-care applications worldwide. They’re also lightweight, easy to sterilize, and come with robust after-sales support.
Whether you're a solo practitioner or a hospital buyer, investing in the best handheld ultrasound machine enhances your clinical efficiency, patient experience, and diagnostic capabilities.
🟦 24. Handheld Wireless Color Doppler Ultrasound for OB-GYN
A handheld wireless color Doppler ultrasound for OB-GYN is an indispensable tool for obstetricians and gynecologists. This compact, mobile device enables rapid and accurate imaging of the uterus, ovaries, fetus, and placenta—anytime and anywhere.
The device supports Color Doppler and Pulsed Wave Doppler, allowing real-time assessment of fetal heart rate, umbilical cord flow, uterine artery flow, and endometrial health. It connects wirelessly to smartphones or tablets, offering convenience in outpatient visits, labor rooms, or remote settings.
Its small size and user-friendly interface make it ideal for antenatal check-ups, early pregnancy scans, follicular monitoring, and postpartum assessments. The high-resolution imaging enhances fetal visualization, maternal-fetal safety, and clinical confidence.
Because it’s wireless and battery-operated, the OB-GYN handheld ultrasound is perfect for mobile clinics, telemedicine, and emergency care. Many models also support image storage, cloud backup, and EMR integration, ensuring better patient documentation and care continuity.
In short, this tool modernizes OB-GYN practice by offering flexibility, speed, and quality diagnostics directly in the hands of clinicians.
🟦 25. Handheld Wireless Color Doppler Ultrasound for Emergency Medicine
In emergency medicine, handheld wireless color Doppler ultrasound is a lifesaver—literally. This compact imaging device allows doctors to assess critical conditions quickly at the point of care, improving response times and outcomes.
From trauma cases to cardiac emergencies, the device enables real-time evaluation of internal bleeding, organ damage, pericardial effusion, and vascular flow. With color Doppler capabilities, clinicians can visualize blood flow patterns and detect clots, obstructions, or aneurysms instantly.
Wireless functionality allows the ultrasound to connect with mobile devices, making it easy to carry, disinfect, and operate during fast-paced situations. Its portability is crucial in ERs, ambulances, field hospitals, and disaster response zones.
These ultrasounds often include rechargeable batteries, multi-head probes, and AI-enhanced imaging—all contributing to faster decision-making and lifesaving care. Whether diagnosing pneumothorax or confirming cardiac arrest, the handheld ultrasound provides essential insights in seconds.
For emergency physicians, paramedics, and trauma teams, this tool delivers the power of diagnostics right where it’s needed most.
🟦 26. Handheld Wireless Color Doppler Ultrasound for Cardiology
A handheld wireless color Doppler ultrasound for cardiology has revolutionized heart imaging by making it portable, accessible, and efficient. Cardiologists can now assess cardiac function, chamber size, wall motion abnormalities, pericardial effusion, and blood flow in real-time, right at the bedside.
These devices offer Color Doppler and Pulsed Wave Doppler modes, enabling detailed visualization of blood flow patterns within the heart and major vessels. This makes it easier to identify conditions like valvular disease, congenital defects, or congestive heart failure early.
The wireless feature allows connection with smartphones and tablets, streamlining image sharing, reporting, and telecardiology. Physicians can save, review, and forward scans to specialists instantly, improving collaborative diagnosis and reducing the time to treatment.
Lightweight and easy to use, handheld cardiac ultrasounds are ideal for outpatient visits, ICUs, emergency departments, and remote cardiac camps. With rechargeable batteries and waterproof probes, they deliver dependable imaging without bulky equipment.
This innovation enhances point-of-care cardiology, especially in low-resource settings, by empowering clinicians to perform quick and accurate heart assessments anywhere.
🟦 27. Handheld Ultrasound for Vascular Imaging
A handheld ultrasound for vascular imaging provides a powerful solution for examining arteries and veins in a fast, convenient, and cost-effective manner. It is widely used in the diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis (DVT), carotid artery disease, and peripheral arterial disease (PAD).
Equipped with color Doppler and high-frequency linear probes, these devices visualize blood flow, detect blockages, and assess vessel patency accurately. Clinicians can perform bedside vascular assessments and make immediate decisions regarding anticoagulation, intervention, or further imaging.
The handheld ultrasound is portable and wireless, making it perfect for vascular clinics, emergency rooms, and surgical wards. Its ease of use and high-resolution imaging also make it ideal for follow-ups after vascular procedures or stent placements.
Many devices include AI-assisted features for auto-measuring flow velocities and diameters. They support image saving and integration with hospital records, enhancing workflow efficiency.
For vascular surgeons and interventional radiologists, a handheld Doppler ultrasound device enhances diagnostic speed and precision, ensuring better outcomes for patients with vascular conditions.
🟦 28. Wireless Ultrasound for Rural Clinics
Wireless ultrasound for rural clinics is bridging the healthcare gap by bringing advanced diagnostic tools to underserved and remote areas. Compact, portable, and battery-powered, these handheld devices allow physicians and healthcare workers to perform accurate ultrasound scans without needing traditional hospital setups.
With color Doppler functionality, these devices can evaluate internal organs, fetal development, heart conditions, and vascular health on the spot. Their wireless nature means they connect directly to smartphones or tablets, eliminating bulky consoles and enabling mobility.
Rural clinics benefit from this innovation as it allows timely diagnosis, reduces unnecessary referrals, and improves patient care. Doctors can use it during regular checkups, emergency visits, or maternity care with ease.
Furthermore, wireless ultrasounds often support telemedicine by allowing live scanning or sharing images with urban specialists for second opinions. This increases confidence in diagnoses and leads to quicker treatment decisions.
Wireless ultrasound is more than a tool—it’s a game-changer for rural healthcare, empowering clinics with modern diagnostics and reducing inequalities in access to quality care.
🟦 29. Handheld Ultrasound for Internal Medicine
Handheld ultrasound for internal medicine has become an essential diagnostic extension for physicians practicing primary care, nephrology, hepatology, and more. It enables bedside assessment of the lungs, heart, abdomen, kidneys, bladder, and vascular system.
Internists use it to evaluate pleural effusions, ascites, gallstones, hydronephrosis, liver disease, and more in real-time, which speeds up diagnosis and reduces reliance on radiology departments.
These handheld devices come with multiple imaging modes including B-mode and color Doppler. With linear, convex, and phased array probes, internists can perform detailed assessments across organ systems using one compact tool.
Wireless functionality allows seamless connection to mobile apps where doctors can store images, create reports, and share results instantly. Its small size and portability make it ideal for outpatient clinics, hospital wards, and home visits.
By integrating handheld ultrasound into daily practice, internal medicine physicians can make faster, more confident clinical decisions and improve patient outcomes—especially in resource-limited or time-sensitive environments.
🟦 30. Wireless Ultrasound for Primary Care
Wireless ultrasound for primary care is redefining how general practitioners deliver frontline healthcare. Traditionally dependent on lab tests and referrals, primary care physicians can now perform real-time diagnostic scans during routine appointments.
This compact tool enables quick evaluation of common complaints like abdominal pain, joint swelling, early pregnancy, urinary retention, and soft tissue injuries. With color Doppler imaging, it can also assess vascular issues like DVT and varicose veins.
Wireless ultrasounds connect to mobile devices and are easy to operate, making them perfect for busy primary care settings. They help reduce diagnostic delays, increase patient satisfaction, and enhance decision-making in a single visit.
Moreover, primary care doctors can use wireless ultrasounds to triage patients better and prioritize emergency cases. With telemedicine integration, they can consult specialists remotely using live scans or recorded images.
Incorporating wireless ultrasound into primary care elevates diagnostic capabilities and reduces patient referrals—making healthcare more accessible, efficient, and affordable.
🟦 31. Handheld Ultrasound with Linear Probe
A handheld ultrasound with linear probe is an essential tool for high-resolution imaging of superficial structures. Linear probes operate at higher frequencies, making them ideal for vascular studies, musculoskeletal assessments, thyroid scans, and soft tissue imaging.
Portable and wireless, these devices provide real-time, color Doppler-enhanced images right on a smartphone or tablet. Physicians can quickly assess vein compressibility for DVT, tendon injuries, lymph nodes, or guide procedures like nerve blocks and biopsies with ease.
Linear probes offer excellent axial and lateral resolution, making them a reliable tool in emergency rooms, outpatient clinics, sports medicine, and bedside care. Their compact size ensures they fit into a physician’s coat pocket, and their wireless nature allows use in sterile settings without cables.
The integration of AI auto-measurements and remote consultation features also enables faster, more accurate diagnostics. For point-of-care practitioners, a handheld ultrasound with a linear probe boosts clinical efficiency and patient satisfaction.
🟦 32. Wireless Ultrasound for Lung Imaging
Wireless ultrasound for lung imaging has become a key diagnostic tool during the rise of respiratory diseases like pneumonia, pleural effusion, and COVID-19. It offers a non-invasive, radiation-free, bedside solution that’s especially valuable in emergency and ICU settings.
Using a convex or linear probe, physicians can identify B-lines, consolidation, pleural sliding, and effusions with high accuracy. Real-time color Doppler helps assess blood flow to detect pulmonary infarcts or differentiate between effusion types.
Because it's wireless and portable, the device eliminates the need to transport critically ill patients to the radiology department. It connects directly to tablets or smartphones and allows remote review by pulmonologists or intensivists.
For rural or mobile clinics, wireless lung ultrasound is an invaluable tool in triaging and monitoring respiratory conditions. With growing AI assistance, it is also becoming easier for general physicians to interpret lung findings accurately.
🟦 33. Portable Wireless Ultrasound with Color Doppler
A portable wireless ultrasound with color Doppler delivers the power of advanced imaging in the palm of your hand. Designed for speed and mobility, these devices help clinicians assess blood flow, vessel patency, cardiac motion, and organ perfusion—right at the point of care.
With multiple probe options (convex, linear, phased), these devices cater to general, cardiac, vascular, and abdominal applications. The built-in color Doppler shows directional blood flow, helping detect clots, stenosis, or perfusion issues in real time.
Their portability makes them ideal for emergency rooms, ambulance use, telemedicine, and rural health missions. With Bluetooth or WiFi connectivity, users can sync images with mobile apps, share with specialists, or integrate with EMRs instantly.
This innovation enhances diagnostic accuracy, reduces imaging delays, and lowers healthcare costs, especially in areas with limited access to full-sized machines.
🟦 34. Handheld Ultrasound with Convex Probe
A handheld ultrasound with convex probe is ideal for abdominal and OB/GYN imaging due to its deeper penetration and wider field of view. Convex probes, also known as curved array transducers, are designed for visualizing deeper structures such as liver, kidney, uterus, or fetus.
This handheld, wireless setup is compact and lightweight, enabling fast diagnosis at the bedside, in the clinic, or even during home visits. It's perfect for general practitioners, emergency doctors, and midwives.
With color Doppler capability, clinicians can assess blood flow in organs and umbilical arteries during pregnancy. This enhances prenatal care, especially in remote areas where traditional ultrasound systems are not available.
The device connects easily with smartphones or tablets, supports cloud storage, and offers battery-powered operation. A handheld convex ultrasound brings modern imaging to primary care, maternity services, and low-resource settings.
🟦 35. Wireless Ultrasound with Phased Array Probe
A wireless ultrasound with phased array probe is engineered for cardiac and thoracic imaging, offering high frame rates and deep penetration. Phased array transducers are crucial in echocardiography, especially when assessing wall motion, valve function, and pericardial effusion.
These portable devices allow cardiologists and emergency physicians to perform rapid heart assessments at the point of care. The compact design and wireless interface reduce clutter and facilitate use in ICUs, ambulances, and disaster response.
Color Doppler functionality enables visualization of intracardiac flow, valvular regurgitation, and shunts. The ability to pair with mobile devices enhances portability and allows real-time sharing for remote consultation.
In settings where time is critical, a wireless phased array ultrasound empowers clinicians with immediate insights into cardiac function, improving outcomes in acute care and beyond.
🟦 36. Wireless Ultrasound for Anesthesia
Wireless ultrasound for anesthesia improves the safety and success of regional blocks and vascular access procedures. With high-resolution linear probes and color Doppler, anesthesiologists can visualize nerves, arteries, veins, and surrounding structures in real time.
This portable device aids in performing peripheral nerve blocks, epidurals, and central venous catheter insertions with enhanced precision, reducing complications and improving patient comfort.
Wireless functionality allows flexible probe positioning without cord interference—ideal for sterile fields. The images can be viewed on a tablet or smartphone, stored for documentation, or shared instantly with supervising consultants or remote teams.
Whether in operating theaters, ICUs, or pain clinics, wireless ultrasound empowers anesthesiologists with efficient, image-guided care. It minimizes guesswork, enhances safety, and speeds up workflows.
🟦 37. Wireless Ultrasound with Needle Guide
A wireless ultrasound with needle guide is a game-changer for procedures requiring high precision. This feature enables accurate needle visualization during interventions such as nerve blocks, biopsies, fluid aspirations, and vascular access.
The needle guide attachment or software overlay ensures real-time alignment between the probe and the needle path, reducing the learning curve for novice users and increasing confidence in critical procedures.
By being wireless, the device ensures freedom of movement, easier probe handling, and no risk of wire contamination in sterile fields. It can display on mobile screens, allowing assistants or supervisors to observe the procedure remotely.
In emergency medicine, anesthesia, and interventional radiology, this capability enhances procedural success, reduces complications, and shortens procedural time.
🟦 38. Wireless Ultrasound for Pain Management
Wireless ultrasound for pain management enables accurate diagnosis and image-guided interventions for musculoskeletal and neuropathic pain conditions. Using high-frequency linear probes, clinicians can identify trigger points, nerve entrapments, joint effusions, and tendon injuries.
Color Doppler helps avoid vessels during injections and assess inflammation. Real-time visualization improves the efficacy of corticosteroid, PRP, or nerve block injections, increasing patient comfort and reducing risks.
Wireless operation and mobile device integration provide flexibility and quick documentation. Pain specialists can use these devices in outpatient clinics, rehab centers, or even during home visits.
By incorporating wireless ultrasound into pain management, physicians can deliver targeted, evidence-based treatments that improve outcomes and reduce medication dependency.
🟦 39. Wireless Ultrasound for Abdominal Imaging
Wireless ultrasound for abdominal imaging is a vital diagnostic tool that fits in your pocket. It allows clinicians to evaluate the liver, gallbladder, kidneys, bladder, pancreas, spleen, and aorta on-site, without needing a bulky ultrasound machine.
The convex probe offers deep penetration, while color Doppler adds real-time blood flow assessment—essential for detecting conditions like AAA, liver cirrhosis, hydronephrosis, or gallstones.
This wireless tool is ideal for emergency rooms, general practice, and remote health centers. It enables faster diagnosis of abdominal pain, trauma, or infections and supports safe monitoring of chronic conditions.
With easy connectivity to mobile apps, wireless abdominal ultrasound allows quick reporting, storage, and teleconsultation, enhancing patient care across all healthcare settings.
🟦 40. Wireless Ultrasound with AI Features
Wireless ultrasound with AI features brings the power of intelligent diagnostics into a clinician’s pocket. These devices are equipped with advanced software that assists with image interpretation, auto-measurements, and organ recognition.
AI helps detect anomalies in heart function, fetal growth, vascular flow, and organ size with minimal user input. It can automatically calculate ejection fraction, estimate gestational age, or highlight abnormal fluid accumulation.
This reduces operator dependency, improves consistency, and makes the device usable even for beginners or non-radiologists. The wireless design ensures mobility, while cloud integration allows sharing and remote collaboration.
For busy hospitals and clinics, AI-powered wireless ultrasound streamlines workflows, shortens learning curves, and enhances the quality of care delivered—especially at the point of care.
🟦 41. Wireless Ultrasound with Rechargeable Battery
A wireless ultrasound with rechargeable battery brings unmatched portability to diagnostic imaging. These compact devices are designed for mobility, allowing clinicians to perform high-quality ultrasounds anywhere without being tethered to power cords.
The built-in lithium-ion battery typically offers 3–5 hours of continuous scanning. This feature is essential for doctors working in emergency response, remote rural healthcare, mobile clinics, or even in patient homes. It’s especially useful in resource-limited settings where electricity access is unreliable.
These devices connect to smartphones, tablets, or laptops via Wi-Fi or Bluetooth and support real-time color Doppler imaging. The rechargeable design ensures reduced downtime, and most models recharge quickly via USB-C or wireless docks.
With efficient power management, this innovation supports sustainable healthcare, enabling accurate point-of-care diagnosis without reliance on heavy, power-dependent machines.
🟦 42. Wireless Ultrasound with Dual Probe
A wireless ultrasound with dual probe combines two transducers—typically convex and linear—into one device, providing versatility in clinical imaging. This all-in-one solution allows physicians to scan both deep and superficial structures without switching devices.
The convex probe is ideal for abdominal and obstetric imaging, while the linear probe offers high-resolution scans for vascular, musculoskeletal, and soft tissue exams. A dual-probe device saves time, reduces equipment clutter, and enhances workflow efficiency.
Wireless operation ensures easy movement around the patient, and real-time color Doppler imaging assists in blood flow analysis. Dual-probe ultrasounds are highly valuable in emergency care, primary care, sports medicine, and telemedicine.
Compact, durable, and rechargeable, this innovation is reshaping how healthcare providers conduct fast, accurate assessments in any clinical environment.
🟦 43. Wireless Ultrasound for Pediatrics
Wireless ultrasound for pediatrics is a safe, non-invasive, and radiation-free imaging option tailored for children. With high-frequency linear probes and intuitive design, these portable tools are perfect for neonatal, infant, and child assessments.
In pediatric care, ultrasound is commonly used to evaluate the brain (through the fontanelle), lungs, abdomen, joints, and urinary tract. Color Doppler enhances the ability to detect blood flow anomalies, congenital heart defects, and vascular malformations.
Wireless operation means minimal disturbance to young patients, as clinicians can conduct exams at the bedside or in parents’ arms. Pediatricians, neonatologists, and emergency doctors benefit from instant, mobile diagnostics.
This compact, lightweight device improves comfort and outcomes in pediatric imaging, making it a must-have in modern children’s hospitals and NICUs.
🟦 44. Wireless Ultrasound for Obstetrics and Gynecology
Wireless ultrasound for obstetrics and gynecology (OB/GYN) has revolutionized women’s healthcare. These pocket-sized tools help OB/GYNs monitor fetal development, assess gynecological conditions, and perform early pregnancy scans on the go.
With convex probes and color Doppler, clinicians can evaluate fetal heart rate, placental blood flow, and uterine abnormalities. Wireless connectivity to smartphones or tablets ensures rapid documentation and teleconsultation.
Portable OB/GYN ultrasound is particularly beneficial for midwives, rural clinics, and antenatal outreach programs. It enables safe, cost-effective care, even in low-resource areas.
This technology enhances patient trust and experience while supporting early diagnosis and informed clinical decisions in women’s health.
🟦 45. Wireless Ultrasound with Waterproof Design
A wireless ultrasound with waterproof design adds an extra layer of safety and durability to clinical imaging. Whether used in surgical theaters, ICUs, or emergency situations, waterproofing allows easy sterilization and safe operation in fluid-rich environments.
These probes typically meet IPX7 or higher ratings, allowing submersion in disinfectants or saline. Waterproofing prevents fluid infiltration and extends device life, especially during wound care, interventional procedures, or OB/GYN exams.
Despite the robust design, image quality remains excellent, with high-resolution imaging and real-time color Doppler features.
This design makes handheld wireless ultrasounds more reliable in high-stakes or infection-sensitive areas, supporting safer patient care across all specialties.
🟦 46. Wireless Ultrasound with Fast Boot Time
A wireless ultrasound with fast boot time is crucial for time-sensitive clinical environments like emergency rooms, trauma bays, or ambulances. Quick power-up—usually under 10 seconds—means clinicians can perform critical scans without delay.
These devices are powered by efficient processors and solid-state memory, allowing instant connectivity to mobile apps and cloud services. With one-click access, doctors can immediately begin scanning for internal bleeding, cardiac arrest assessment, or fetal heart monitoring.
Combined with portability and color Doppler, fast booting enhances point-of-care performance, reduces patient wait times, and improves outcomes, particularly in acute care and pre-hospital settings.
🟦 47. Wireless Ultrasound for Internal Medicine
Wireless ultrasound for internal medicine is becoming a standard diagnostic tool for internists and primary care physicians. It assists in evaluating abdominal organs, lungs, heart, kidneys, and blood vessels without sending patients to imaging departments.
Handheld ultrasound helps detect ascites, gallstones, hydronephrosis, pleural effusions, and even early heart failure. With color Doppler, internists can assess perfusion, identify DVT, or evaluate hepatic vasculature.
Wireless and app-enabled, these tools fit seamlessly into outpatient workflows and home visits. They promote faster decision-making and reduce unnecessary referrals or tests.
By bringing imaging into the internist’s hands, wireless ultrasound empowers more comprehensive, on-the-spot care.
🟦 48. Wireless Ultrasound for Mobile Clinics
Wireless ultrasound for mobile clinics delivers high-quality diagnostics to underserved and remote populations. Compact, battery-powered, and app-connected, these devices help bridge healthcare gaps with affordable imaging on wheels.
Whether assessing pregnancies, cardiac conditions, abdominal pain, or infections, mobile clinics can now perform real-time color Doppler scans on-site. These ultrasounds support telemedicine collaboration and patient record integration via cloud platforms.
Lightweight and easy to carry, they reduce the need for hospital visits, saving time and cost for both providers and patients.
In humanitarian aid, disaster response, or outreach programs, wireless ultrasound enhances diagnostic capabilities and improves healthcare equity.
🟦 49. Wireless Ultrasound with Remote Access
A wireless ultrasound with remote access feature allows real-time image sharing with specialists, making it ideal for telemedicine and collaborative diagnosis. These devices stream live ultrasound scans over secure cloud platforms, enabling remote guidance and second opinions.
Doctors in rural or isolated areas can consult radiologists or specialists in real time, improving diagnostic confidence and treatment accuracy. Remote mentoring is also valuable for training new practitioners.
Color Doppler imaging and AI assistance can be viewed simultaneously on connected devices, ensuring team-based care. With HIPAA-compliant platforms, patient privacy is maintained.
This connectivity transforms how ultrasound services are delivered, making expert care more accessible and efficient.
🟦 50. Wireless Ultrasound with Image Storage
A wireless ultrasound with image storage feature helps clinicians capture, review, and archive diagnostic scans for documentation and follow-up. Most devices store images on mobile apps or cloud platforms, offering seamless integration with electronic medical records (EMRs).
Image storage allows physicians to track disease progression, monitor treatment outcomes, and ensure legal documentation. It also facilitates patient education by displaying previous scan comparisons.
With wireless transmission and color Doppler functionality, stored images maintain diagnostic quality. Doctors can annotate, export, or share images for consultation or training purposes.
This feature boosts clinical efficiency, enhances patient trust, and streamlines recordkeeping—essential for modern healthcare delivery.
🟦 51. Wireless Ultrasound with Real-Time Imaging
A wireless ultrasound with real-time imaging enables clinicians to instantly visualize internal anatomy and physiological functions during examinations. This capability is vital for fast, point-of-care diagnostics.
Whether assessing cardiac function, detecting fluid collections, or guiding needle placements, real-time imaging enhances decision-making and procedural accuracy. Wireless connectivity to smartphones or tablets allows smooth streaming and immediate interpretation without delay.
The addition of color Doppler provides dynamic visualization of blood flow, making the technology invaluable for vascular, abdominal, and OB/GYN applications.
This combination of real-time data, mobility, and user-friendly interface is transforming modern medical practice by providing diagnostic power at the patient’s side.
🟦 52. Wireless Ultrasound with Automatic Image Optimization
A wireless ultrasound with automatic image optimization leverages intelligent algorithms to adjust imaging parameters such as gain, depth, contrast, and focus automatically.
This technology enhances ease of use, especially for non-radiologist users such as emergency physicians, GPs, or nurses. It allows clear, high-resolution imaging with minimal user input—perfect for fast-paced clinical settings.
When combined with color Doppler, automatic optimization ensures accurate assessment of blood flow and organ perfusion without technical complexity.
This innovation supports consistent imaging quality, reduces scanning errors, and increases confidence in diagnostic interpretation—especially in rural or resource-limited facilities.
🟦 53. Wireless Ultrasound with Multi-Language Support
A wireless ultrasound with multi-language support enhances accessibility and usability across diverse healthcare environments.
These devices support interfaces in English, Spanish, Chinese, Arabic, French, and many more—making them adaptable for global use. This is especially important in international NGOs, telemedicine platforms, or multi-ethnic hospital settings.
Multi-language compatibility also helps in training, onboarding, and reducing the learning curve for new users.
With real-time color Doppler, intuitive design, and mobile connectivity, these ultrasounds promote inclusive diagnostics and efficient cross-border deployment—bridging linguistic gaps in healthcare delivery.
🟦 54. Wireless Ultrasound for Lung Imaging
Wireless ultrasound for lung imaging has become essential for diagnosing and monitoring pulmonary conditions such as pneumonia, pleural effusion, pulmonary edema, and pneumothorax.
With a linear or convex probe and real-time color Doppler, doctors can evaluate lung sliding, B-lines, effusions, and consolidations right at the bedside.
Portable, battery-powered design makes it ideal for ICUs, emergency rooms, and even home visits during COVID-19 follow-up or chronic care.
Wireless lung ultrasound is safe, fast, and radiation-free—empowering pulmonologists, internists, and GPs to make timely, accurate respiratory assessments at the point of care.
🟦 55. Wireless Ultrasound with Telemedicine Integration
A wireless ultrasound with telemedicine integration allows healthcare providers to connect remotely with specialists while performing ultrasound exams.
Live video streaming of real-time scans via secure platforms lets remote experts guide procedures or verify diagnoses. It is particularly valuable in rural clinics, disaster zones, or ships where no on-site radiologist is available.
Combined with color Doppler, this feature supports collaborative interpretation and faster patient care. Integration with EMRs and cloud storage ensures secure recordkeeping and continuity of care.
This solution expands access to quality diagnostics and boosts clinical efficiency in a rapidly evolving telehealth ecosystem.
🟦 56. Wireless Ultrasound for Emergency Medicine
Wireless ultrasound for emergency medicine is a game-changer in trauma bays, ambulances, and ERs. It enables physicians to perform FAST (Focused Assessment with Sonography in Trauma), cardiac, abdominal, and lung scans on the spot.
Handheld wireless devices connect to mobile apps and deliver real-time images with color Doppler for quick assessment of bleeding, fluid accumulation, or cardiac activity.
Portability, fast boot-up, and intuitive interface make these devices indispensable for time-critical decisions—saving lives when every second counts.
They reduce dependence on central imaging departments and provide diagnostic autonomy in high-pressure settings.
🟦 57. Wireless Ultrasound with Needle Guidance
A wireless ultrasound with needle guidance provides accurate, real-time visualization for procedures like central line placement, nerve blocks, biopsies, and abscess drainage.
With built-in needle enhancement mode and color Doppler, these devices highlight needle trajectories and blood vessels to avoid complications.
Wireless design allows unhindered maneuvering, while mobile app interfaces enable one-touch recording and annotation.
This tool improves safety, efficiency, and success rates in interventional procedures across ERs, ICUs, operating rooms, and outpatient clinics.
🟦 58. Wireless Ultrasound with Cloud Storage
A wireless ultrasound with cloud storage enables clinicians to save, review, and share ultrasound data securely. This feature ensures that important diagnostic images and videos are accessible anytime, from any device.
Doctors can archive exams, track patient progress, and collaborate with remote specialists—all without worrying about data loss.
Most platforms offer HIPAA-compliant encryption, customizable access levels, and integration with telemedicine tools.
Combined with real-time color Doppler imaging, cloud storage supports a more efficient, collaborative, and paperless healthcare workflow.
🟦 59. Wireless Ultrasound with AI-Powered Diagnostics
A wireless ultrasound with AI-powered diagnostics uses machine learning algorithms to automatically detect abnormalities, suggest diagnoses, and guide novice users through image acquisition.
AI enhances accuracy, reduces training needs, and speeds up diagnostic workflow. From measuring fetal growth to identifying heart chamber abnormalities, these tools are transforming point-of-care imaging.
With wireless portability, color Doppler, and AI interpretation combined, clinicians can offer more precise and consistent care—even in remote settings.
This innovation is paving the way for democratized, intelligent ultrasound use in the 21st century.
🟦 60. Wireless Ultrasound for Veterinary Medicine
Wireless ultrasound for veterinary medicine is increasingly popular among animal healthcare professionals. It allows portable, stress-free imaging of pets, livestock, and even wildlife in field conditions.
Veterinarians use these tools to evaluate the abdomen, reproductive organs, heart, and musculoskeletal system. Wireless design and mobile display let vets scan comfortably without restraining animals harshly.
Color Doppler adds value in assessing blood flow, pregnancy monitoring, and cardiac conditions.
With waterproof casing, long battery life, and quick startup, handheld wireless ultrasound is a perfect diagnostic companion in animal hospitals and farms.
🟦 61. Wireless Ultrasound for Obstetrics and Gynecology
Wireless ultrasound for obstetrics and gynecology is revolutionizing maternal healthcare by providing portable, real-time fetal and uterine imaging. Obstetricians use it to monitor fetal growth, amniotic fluid, placental location, and fetal heartbeat, while gynecologists can evaluate ovarian cysts, fibroids, and uterine abnormalities.
The handheld, wireless format allows flexibility during prenatal checkups at the bedside or in remote health camps. Integration with mobile apps enables easy image sharing, reporting, and follow-up.
With color Doppler, it becomes even more powerful—helping assess fetal circulation, umbilical cord blood flow, and uteroplacental perfusion. It enhances early diagnosis and improves patient outcomes in both routine and high-risk pregnancies.
🟦 62. Wireless Ultrasound for Cardiology
Wireless ultrasound for cardiology provides real-time cardiac imaging in a compact and mobile format. Cardiologists can assess heart size, valve function, pericardial effusion, and ejection fraction using handheld probes connected to smartphones or tablets.
This is particularly valuable in outpatient clinics, emergency rooms, and ICUs. The portability enables rapid bedside echocardiography (POCUS), reducing delays in heart failure, myocardial infarction, and arrhythmia assessments.
Color Doppler helps visualize blood flow patterns, valvular regurgitation, and intracardiac shunts. This affordable, accessible tool increases diagnostic capabilities beyond the echo lab—transforming frontline cardiac care.
🟦 63. Wireless Ultrasound for Musculoskeletal Imaging
Wireless ultrasound for musculoskeletal (MSK) imaging is a powerful tool for diagnosing soft tissue injuries, joint effusions, tendon tears, and nerve compressions.
Orthopedic surgeons, sports medicine specialists, and physiotherapists use it to visualize structures in real time—guiding injections or monitoring healing after injury.
Wireless connectivity makes it ideal for on-the-field use or in busy outpatient departments. The high-resolution linear probe and color Doppler provide precise visualization of muscles, tendons, and surrounding vasculature.
It enhances clinical decision-making, reduces MRI dependence, and speeds up injury management with immediate insights.
🟦 64. Wireless Ultrasound for Anesthesia
Wireless ultrasound for anesthesia has become an essential component for regional blocks, vascular access, and perioperative monitoring.
Anesthesiologists use wireless linear probes for nerve localization during procedures like brachial plexus or femoral nerve blocks. Real-time guidance enhances block accuracy and reduces complications.
Color Doppler helps avoid vascular injury by identifying arteries and veins during needle insertion. The wireless design offers better maneuverability in the sterile field and improves ergonomics in tight OR spaces.
With mobile screen support and image recording, it elevates safety and efficiency in modern anesthesia practice.
🟦 65. Wireless Ultrasound for Pediatrics
Wireless ultrasound for pediatrics offers a child-friendly, fast, and safe diagnostic method. It reduces the need for radiation-based imaging like X-rays or CT scans in infants and children.
Pediatricians can assess conditions like intussusception, pyloric stenosis, hydrocephalus, and urinary tract anomalies using a handheld ultrasound.
Its small size, fast scanning, and wireless design minimize stress for both children and parents. Color Doppler adds further diagnostic value by showing organ perfusion and vascular abnormalities.
From outpatient clinics to emergency departments, pediatric wireless ultrasound supports better, gentler care for young patients.
🟦 66. Wireless Ultrasound for Urology
Wireless ultrasound for urology assists in evaluating the kidneys, bladder, prostate, and testicles. Urologists can diagnose hydronephrosis, bladder retention, prostate enlargement, and scrotal conditions instantly at the patient’s side.
Portable handheld devices allow fast bedside assessment during emergencies or follow-ups. Real-time color Doppler helps evaluate blood flow in renal vessels or testicular torsion cases.
With easy image storage and reporting, wireless ultrasound improves workflow in busy clinics while reducing dependency on external imaging centers.
It enhances efficiency, patient satisfaction, and accuracy in urologic evaluations.
🟦 67. Wireless Ultrasound for Abdominal Scans
Wireless ultrasound for abdominal scans enables rapid, non-invasive assessment of internal organs such as the liver, gallbladder, kidneys, pancreas, spleen, and intestines.
It is used in general practice, internal medicine, and emergency care to detect stones, cysts, masses, ascites, or organomegaly.
The wireless feature allows clinicians to scan patients in wards, ICUs, or even at home visits. Coupled with color Doppler, it provides information on blood flow in abdominal vessels, tumors, and inflammatory processes.
This is a game-changer in resource-limited or remote settings where access to traditional sonography is limited.
🟦 68. Wireless Ultrasound with 3-in-1 Probe
A wireless ultrasound with a 3-in-1 probe integrates convex, linear, and phased array functions into one compact device—ideal for doctors who need versatility in scanning.
Convex is used for abdominal and obstetric scans, linear for vascular and MSK, and phased array for cardiac imaging. With just one probe, clinicians can handle diverse diagnostic needs across departments.
The wireless and pocket-sized design means easy portability, especially for field work or house calls. Color Doppler across all three modes enhances diagnostic power.
This multifunctional solution reduces equipment costs and simplifies clinical workflows.
🟦 69. Wireless Ultrasound with Freeze and Store Function
A wireless ultrasound with freeze and store function allows clinicians to pause the live image, capture the frame, and save it instantly for review or documentation.
This feature is vital in capturing fleeting views of moving structures like the heart or fetus. It also supports telemedicine consultations and report generation.
Users can annotate images, export to PDF, or upload to cloud systems directly from their mobile device. Combined with color Doppler, clinicians can capture and analyze vascular data accurately.
It ensures accurate recordkeeping and supports evidence-based medical decisions.
🟦 70. Wireless Ultrasound with Rechargeable Battery
A wireless ultrasound with rechargeable battery enhances mobility and convenience in any clinical setting. These devices often run for 2–6 hours on a single charge and are quickly recharged via USB or docking stations.
They are ideal for use in ambulances, rural clinics, home care, and mobile health camps where power supply may be limited.
Battery-powered operation means no dependency on wall outlets or bulky cords. The built-in color Doppler still delivers high-quality vascular imaging on the go.
Such flexibility empowers frontline healthcare workers and boosts diagnostic outreach in underserved areas.
🟦 71. Wireless Ultrasound Machine with Mobile App
A wireless ultrasound machine with mobile app connects seamlessly with smartphones or tablets, offering real-time imaging and diagnostic capabilities anytime, anywhere. Through Wi-Fi or Bluetooth, the ultrasound probe sends high-resolution images directly to a compatible mobile app.
Doctors can scan, freeze, annotate, store, and even share images instantly. The app often includes AI assistance, auto-measurements, and cloud integration—streamlining clinical workflow.
The color Doppler function embedded in the probe lets clinicians assess blood flow and vascular health efficiently. This fusion of wireless hardware and smart software is revolutionizing point-of-care diagnostics in both urban hospitals and rural outreach programs.
🟦 72. Wireless Ultrasound for Sports Medicine
Wireless ultrasound for sports medicine provides immediate imaging of muscle, ligament, tendon, and joint injuries on the field or in clinics. Athletes can be assessed instantly without waiting for MRI or radiology referrals.
Sports physicians use linear probes to examine soft tissues and guide injections precisely. Color Doppler imaging allows for assessment of inflammation or vascular damage associated with injuries.
Compact and cable-free, these ultrasound devices are ideal for physical therapy centers, gyms, and even sports events. Quick diagnostics aid in faster recovery decisions, enhancing athletic performance and injury prevention strategies.
🟦 73. Wireless Ultrasound for Vascular Surgery
Wireless ultrasound for vascular surgery is a powerful tool for preoperative and postoperative vascular assessment. Surgeons can evaluate carotid arteries, deep veins, peripheral arteries, and grafts quickly using color Doppler technology.
Handheld wireless probes eliminate bulky setups in the OR and improve intraoperative visualization. The color Doppler function provides real-time data on blood flow, stenosis, thrombosis, or graft patency.
This tool is invaluable during vascular access procedures, AV fistula creation, and DVT evaluation. Its portability and accuracy reduce diagnostic delays and elevate vascular care in both surgery and follow-up clinics.
🟦 74. Wireless Ultrasound with AI Integration
Wireless ultrasound with AI integration combines smart technology with compact hardware to deliver automated diagnostics and image analysis. AI helps with measurements like fetal biometry, cardiac output, bladder volume, and more.
Doctors, especially in primary care or remote settings, benefit from real-time scanning support and AI-guided image interpretation. This reduces human error, speeds up diagnosis, and enhances training for junior practitioners.
Color Doppler imaging, supported by AI, can automatically detect abnormal flow patterns, narrowing or occlusions. This next-generation ultrasound setup empowers clinicians with more accurate, data-driven decisions at the point of care.
🟦 75. Wireless Ultrasound for Lung Scans
Wireless ultrasound for lung scans became a game-changer during the COVID-19 pandemic and remains vital for diagnosing pleural effusion, pneumonia, pneumothorax, and pulmonary edema.
With a convex or phased array probe, clinicians can perform bedside lung ultrasonography in ICUs, ERs, or even home settings. The portability reduces infection risks associated with moving critically ill patients.
Color Doppler enhances assessment of pulmonary vascularization and helps identify complications. The ability to connect with mobile apps and save images supports patient monitoring and telemedicine consultations.
This tool offers a safe, quick, and effective way to evaluate respiratory conditions.
🟦 76. Wireless Ultrasound for Emergency Rooms
Wireless ultrasound for emergency rooms (ER) is crucial for rapid diagnosis of trauma, cardiac arrest, internal bleeding, or organ damage. Emergency physicians can use POCUS (Point-of-Care Ultrasound) to guide life-saving decisions.
A wireless probe enables fast bedside scanning without the hassle of cords or large machines. The FAST (Focused Assessment with Sonography in Trauma) exam can be conducted within seconds to detect internal bleeding.
Color Doppler allows assessment of blood flow to major organs or limbs. The device’s mobility and speed make it indispensable in high-pressure ER environments, improving triage and treatment accuracy.
🟦 77. Wireless Ultrasound for Portable Scanning
Wireless ultrasound for portable scanning allows healthcare professionals to conduct real-time imaging anywhere—at a patient’s home, rural clinic, disaster zone, or ambulance.
Its lightweight design and wireless operation eliminate the need for heavy trolleys or wall power. Clinicians can connect it to their smartphone or tablet and begin scanning instantly.
Color Doppler enhances diagnostic power, allowing visualization of blood flow and vascular abnormalities on the spot. This mobility is transforming access to quality imaging in both developed and resource-limited settings—supporting more equitable healthcare delivery.
🟦 78. Wireless Ultrasound for Internal Medicine
Wireless ultrasound for internal medicine empowers internists to perform quick, reliable scans during daily rounds or clinic visits. It aids in evaluating the abdomen, lungs, heart, thyroid, bladder, and blood vessels.
With handheld probes, internists can diagnose ascites, gallstones, cardiac issues, pleural effusion, and more within minutes. The color Doppler feature helps assess vascular status and organ perfusion.
Wireless connectivity allows easy image sharing with specialists, even during teleconsultations. This enhances clinical judgment, reduces patient wait times, and supports more personalized and immediate medical care.
🟦 79. Wireless Ultrasound for Remote Clinics
Wireless ultrasound for remote clinics brings advanced diagnostic capabilities to underserved regions. These devices are ideal for mobile health units, rural hospitals, and international health missions.
Without relying on large machines or power infrastructure, healthcare workers can perform obstetric, cardiac, abdominal, and vascular scans using a single handheld probe.
Color Doppler adds functionality for assessing fetal circulation, DVT, varicose veins, and blood flow in organ transplants. Integration with mobile apps allows image storage, AI assistance, and cloud sharing—connecting rural clinics with urban specialists.
It’s a breakthrough in bridging healthcare access gaps.
🟦 80. Wireless Ultrasound for House Calls
Wireless ultrasound for house calls allows doctors to offer imaging services at patients’ homes—ideal for elderly, palliative, or immobile patients.
General practitioners, geriatricians, and palliative care doctors can perform bedside scans to monitor heart failure, fluid status, bladder volume, or abdominal pathology.
A wireless probe, paired with a smartphone or tablet, enables immediate diagnostics and remote consultation with specialists if needed. Color Doppler function helps assess perfusion and vascular issues without hospital admission.
This brings compassionate, efficient, and high-quality care directly to the patient’s doorstep—redefining modern home healthcare.
🟦 81. Wireless Ultrasound for Kidney Imaging
Wireless ultrasound for kidney imaging offers a quick, portable solution to diagnose renal pathologies such as hydronephrosis, kidney stones, cysts, or masses.
With a convex probe, clinicians can scan the kidneys in real time at the bedside. Color Doppler helps assess renal artery flow and detect vascular abnormalities like renal artery stenosis.
The wireless design enables easy use in outpatient clinics, emergency settings, or even in patients’ homes. Paired with mobile apps, physicians can store and share images, supporting continuity of care and faster decision-making in nephrology and general practice.
🟦 82. Wireless Ultrasound for Liver Imaging
Wireless ultrasound for liver imaging helps in diagnosing liver diseases like fatty liver, cirrhosis, hepatomegaly, and liver tumors.
The device’s portability allows use in outpatient clinics, liver camps, and even in remote areas. Color Doppler evaluates hepatic and portal vein flow, aiding in staging liver disease and detecting complications like portal hypertension.
Doctors can scan, capture, annotate, and share liver images through a connected smartphone or tablet, improving diagnosis and monitoring. This tool supports hepatologists and general physicians in providing efficient, accessible liver care anywhere.
🟦 83. Wireless Ultrasound with Convex Probe
A wireless ultrasound with convex probe is ideal for abdominal and obstetric imaging. Its curved design allows deep penetration and wide field views of organs like the liver, kidneys, bladder, uterus, and fetus.
Wireless operation allows easy scanning at the bedside or during mobile visits. Paired with mobile apps, users can freeze images, record video, and share findings with remote specialists instantly.
Color Doppler enhances the probe’s function by showing real-time blood flow, which is vital in assessing fetal circulation, renal perfusion, or liver vasculature. This is a must-have tool for general practitioners, OB-GYNs, and ER doctors.
🟦 84. Wireless Ultrasound with Linear Probe
A wireless ultrasound with linear probe is ideal for vascular access, soft tissue evaluation, and superficial organs like the thyroid, testicles, or breast.
With high-frequency imaging, this probe provides excellent resolution for small structures. It’s widely used in emergency rooms, ICUs, and outpatient clinics for guided procedures like nerve blocks or central line insertions.
The wireless model connects easily to a smartphone or tablet, enabling flexible use and easy image sharing. Color Doppler aids in evaluating vascular flow, thrombosis, and varicose veins—making it indispensable in both diagnostics and interventional medicine.
🟦 85. Wireless Ultrasound for OB/GYN
Wireless ultrasound for OB/GYN brings powerful prenatal imaging to clinics, delivery rooms, and rural outreach programs. Using convex probes, clinicians can monitor fetal development, amniotic fluid levels, and placental position on the go.
Color Doppler enables assessment of umbilical cord blood flow and fetal heart rate patterns—critical for managing high-risk pregnancies. These devices are perfect for regular antenatal checkups, especially in mobile health units.
Paired with mobile apps, images can be shared with specialists instantly. The compact, wireless design improves prenatal care accessibility, especially in low-resource or remote environments.
🟦 86. Wireless Ultrasound with Phased Array Probe
Wireless ultrasound with phased array probe is primarily used for cardiac and lung imaging. Its small footprint allows scanning between ribs for clear views of the heart or pleura.
This probe is highly effective in diagnosing heart failure, pericardial effusion, or valvular abnormalities. It’s widely used in ICU, ER, and anesthesia settings for bedside echocardiography and critical care assessments.
Wireless connectivity and color Doppler features enhance the diagnostic power, allowing real-time evaluation of cardiac structures and flow patterns. This device supports quicker, more informed decisions during life-threatening emergencies.
🟦 87. Wireless Ultrasound with Triplex Mode
A wireless ultrasound with triplex mode combines B-mode, Color Doppler, and Pulse Wave Doppler for a comprehensive vascular assessment.
Triplex mode allows clinicians to see anatomy, blood flow direction, and velocity in real-time—essential in evaluating arteries, veins, and heart valves. This is vital in diagnosing DVT, stenosis, and vascular insufficiencies.
The wireless format ensures portability and ease of use in emergency, outpatient, or rural setups. With mobile app integration, triplex imaging data can be stored, analyzed, and shared for multidisciplinary consultations.
🟦 88. Wireless Ultrasound for Rural Health Centers
Wireless ultrasound for rural health centers is revolutionizing medical care in underserved areas. Compact, affordable, and battery-powered, these devices offer essential imaging for maternal care, abdominal pain, trauma, and cardiac assessment.
Healthcare workers can carry a wireless probe to remote locations and scan patients on-site, with real-time images displayed on smartphones or tablets.
Color Doppler adds depth to the diagnostics by showing blood flow, supporting evaluation of fetal health, vascular conditions, and organ perfusion. These devices bridge the diagnostic gap and reduce unnecessary hospital referrals.
🟦 89. Wireless Ultrasound for Remote Monitoring
Wireless ultrasound for remote monitoring allows patients to be evaluated and followed up from their homes, especially those with chronic conditions or post-surgery recovery.
Clinicians can perform periodic scans at the patient’s residence or in telemedicine hubs and share images with specialists. This is particularly useful in heart failure, liver disease, or cancer follow-ups.
The addition of color Doppler helps in assessing blood flow, ensuring real-time tracking of disease progression. It’s a cost-effective and patient-friendly solution for continuous care without frequent hospital visits.
🟦 90. Wireless Ultrasound with Cloud Integration
Wireless ultrasound with cloud integration makes it easier to store, access, and share patient images across departments or locations. The probe connects with mobile apps that sync securely to cloud storage.
Doctors can review past scans, compare changes, and send reports to consultants instantly. This boosts collaboration and continuity in patient care—especially in large hospitals or telehealth setups.
Color Doppler images stored in the cloud can be reviewed anytime for advanced interpretation or second opinions. This modern setup enhances workflow efficiency and builds smarter, digital-first healthcare systems.
🟦 91. Wireless Ultrasound for Point-of-Care Diagnosis
Wireless ultrasound for point-of-care diagnosis empowers clinicians to make fast, informed decisions right at the bedside. It eliminates the delay of sending patients to radiology and waiting for reports.
Physicians can use it for abdominal pain, chest trauma, DVT suspicion, pregnancy checks, and cardiac assessments. Real-time Color Doppler adds blood flow analysis, enabling more accurate and immediate diagnoses.
Wireless design enhances portability, especially in ERs, ICUs, ambulances, or field settings. Its compatibility with mobile devices allows instant sharing with specialists. This tool is reshaping urgent care and bedside medicine.
🟦 92. Wireless Ultrasound for Pediatrics
Wireless ultrasound for pediatrics is a game-changer in child healthcare. Smaller, more sensitive probes are used to assess neonatal lungs, brain (cranial USG), abdomen, hips, and more.
Its non-invasive and radiation-free nature makes it perfect for infants and children. Clinicians can diagnose pyloric stenosis, hydrocephalus, intussusception, and even perform line placements with guidance.
Color Doppler evaluates pediatric blood flow for cardiac or abdominal anomalies. Wireless connectivity means reduced setup time and more comfort for young patients in hospitals, clinics, or even during home visits.
🟦 93. Wireless Ultrasound for Sports Medicine
Wireless ultrasound for sports medicine helps diagnose musculoskeletal injuries quickly. It visualizes muscles, tendons, ligaments, and joints for conditions like sprains, tears, bursitis, or effusions.
Physicians and physiotherapists can use a linear probe to assess soft tissue trauma or monitor healing in athletes. Real-time imaging enables on-field evaluation and rapid decisions.
Color Doppler can assess inflammation and blood flow in soft tissues. The wireless design allows easy transport to stadiums, gyms, or sports centers—making it a crucial tool for injury management and recovery monitoring.
🟦 94. Wireless Ultrasound for Home Care
Wireless ultrasound for home care brings diagnostic imaging into the patient’s living room. It supports chronic disease management, elderly care, and follow-up for post-operative patients.
Doctors or trained caregivers can use the device to scan the heart, lungs, abdomen, or perform vascular assessments. Color Doppler adds functional insight into blood flow and organ perfusion.
The wireless feature enables remote consultation with specialists through telemedicine platforms. It reduces hospital visits and enhances comfort for immobile or elderly patients. This is the future of home-based diagnostics.
🟦 95. Wireless Ultrasound with Dual-Probe Technology
Wireless ultrasound with dual-probe technology combines two transducers—typically linear and convex or phased array—into a single device. This eliminates the need to switch probes for different types of scans.
Clinicians can assess superficial structures and deeper organs with a flip of the probe. It’s ideal for emergency, internal medicine, and primary care settings where versatility is crucial.
Color Doppler with dual-probe support offers complete diagnostic power—from vascular flow to abdominal organ analysis. This compact solution boosts efficiency and minimizes downtime in fast-paced environments.
🟦 96. Wireless Ultrasound with Waterproof Design
A wireless ultrasound with waterproof design is vital for environments where hygiene and cleaning are critical, such as operating rooms, ICUs, and field use.
Waterproof models can be disinfected thoroughly and withstand frequent cleaning—making them perfect for infectious disease wards or emergency medical services.
These devices offer all key imaging functions, including Color Doppler, while being easy to sterilize. Clinicians benefit from both portability and safety, ensuring accurate diagnostics without compromising infection control protocols.
🟦 97. Wireless Ultrasound for Cardiac Screening
Wireless ultrasound for cardiac screening enables rapid evaluation of heart function, valvular abnormalities, pericardial effusion, and heart failure signs using a phased array probe.
It is widely used in cardiology clinics, ICUs, and even in outreach programs. Color Doppler reveals real-time blood flow through the heart chambers and valves, offering detailed hemodynamic insight.
This device supports early detection of cardiovascular issues, and the wireless setup allows for efficient image sharing and documentation. A powerful tool for both screening and monitoring cardiac patients.
🟦 98. Wireless Ultrasound with High Resolution Imaging
Wireless ultrasound with high resolution imaging ensures sharper, clearer visuals of both superficial and deep structures. High-frequency probes deliver detailed images needed in vascular, MSK, and thyroid scans.
The clarity boosts diagnostic confidence, especially in early-stage detection of small lesions, cysts, or clots. Color Doppler adds real-time vascular flow to enhance evaluation further.
Combined with wireless transmission, this makes the device perfect for specialists needing portability without compromising on image quality—ideal for dermatologists, endocrinologists, and vascular surgeons.
🟦 99. Wireless Ultrasound with Telemedicine Support
Wireless ultrasound with telemedicine support is shaping the future of remote diagnostics. Clinicians can scan patients in real-time while streaming the session to a remote expert via secure cloud platforms.
This setup is invaluable for rural clinics, mobile health units, and during pandemic situations. Specialists can guide the scan or analyze saved clips and Doppler readings remotely.
Color Doppler visualizations can be shared live, improving diagnostic precision. This solution bridges the gap between patients and top-tier healthcare, even in the most isolated areas.
🟦 100. Wireless Ultrasound for Anesthesiology
Wireless ultrasound for anesthesiology assists in nerve blocks, vascular access, and regional anesthesia with precision. It allows real-time guidance for spinal, epidural, or peripheral procedures.
The linear probe visualizes nerves, arteries, and target structures, while Color Doppler distinguishes vessels to avoid complications. It improves accuracy, safety, and patient outcomes.
Being wireless and compact, anesthesiologists can carry the device into the OR, ICU, or pain clinic. It speeds up workflow and supports teaching, making it an indispensable modern tool for pain and anesthesia management.